Rising information heart power use continues to make headlines. In my first publish on information heart electrical energy use, I centered on the applied sciences that make AI potential and on broad tendencies in information heart funding and electrical energy demand forecasts out to 2028.
When you subscribe to The Dispatch, that they had an excellent AI energy use explainer in March 2024 that enhances my earlier publish.
Electrical energy Demand Forecasts
Extra demand forecasts within the U.S. and globally recommend rising electrical energy demand. The International Energy Agency forecasts a world common annual development fee of three.4% 2024-2026, 85% of which is able to come from China and outdoors of the set of superior economies. The Electrical Energy Analysis Institute (EPRI) revealed a white paper this previous spring motivated by the sudden development in AI-driven computation:
AI fashions are sometimes rather more energy-intensive than the information retrieval, streaming, and communications functions that drove information heart development over the previous 20 years. At 2.9 watt-hours per ChatGPT request, AI queries are estimated to require 10x the electrical energy of conventional Google queries, which use about 0.3 watt-hours every; and rising, computation-intensive capabilities similar to picture, audio, and video era don’t have any precedent. (EPRI 2024, p. 2)
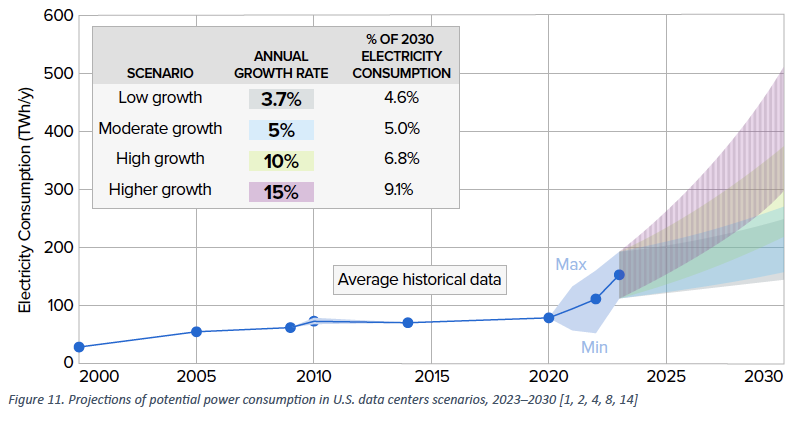
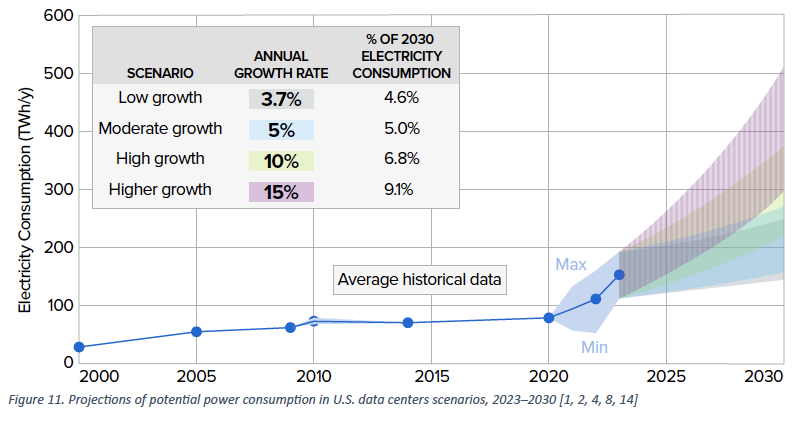
Their evaluation of U.S. demand included low, average, excessive, and better development eventualities by 2030, with electrical energy demand development fee forecasts starting from 3.7% to fifteen%. These eventualities recommend that information heart share of electrical energy demand might be within the vary of 4.6-9.1% of 2030 consumption, in comparison with 4% right this moment (A Might 2024 Axios article supplies a useful abstract of the EPRI evaluation).
Supply: EPRI (2024)
A current Energy Information Administration analysis exhibits that industrial sector electrical energy demand has grown quickest in states with fast computing facility development (together with Virginia and Texas to no shock, however surprisingly additionally together with North Dakota).
Electrical energy demand additionally grew considerably in Texas, the place comparatively low prices for electrical energy and land have attracted a excessive focus of knowledge facilities and cryptocurrency mining operations. North Dakota stands out with the quickest relative development at 37% (up 2.6 BkWh) between 2019 and 2023, attributed to the establishment of large computing facilities in the state. As well as, western states similar to Arizona and Utah have proven strong development in industrial electrical energy demand, additional contributing to the general improve within the prime 10 states. (EIA Right this moment In Power 6-28-2024).
Marshall’s Mannequin of Time, Illustrated By Fishing
Some fundamental financial evaluation will assist us perceive what’s taking place and why, and likewise what to anticipate. For this evaluation I’m going to get some assist from pioneering economist Alfred Marshall.
Supply: Wikipedia
First, let’s collect the information we wish to perceive:
- Technological change is resulting in a rise in information heart computing, which is creating an elevated stage of demand and a quicker development fee of demand for electrical energy.
- Constructing an information heart requires excessive capital expenditure and takes 18-24 months.
- Constructing new electrical energy infrastructure (era, poles, wires, transformers) requires excessive capital expenditure and within the present regulatory and enterprise construction takes as much as 10 or even 20 years.
- New useful resource interconnection with a regional transmission grid can take on average 3.5 years in ERCOT in Texas and up to 6 or more years in other regions. The distinction is the establishments, or guidelines, that ERCOT uses called “connect and manage”.
Now let’s carry Marshall in. Based on Wikipedia, “Alfred Marshall (26 July 1842 – 13 July 1924) was an English economist, and was probably the most influential economists of his time. His guide Principles of Economics (1890) was the dominant financial textbook in England for a few years. It introduced the concepts of supply and demand, marginal utility, and costs of production right into a coherent entire. He is called one of many founders of neoclassical economics.” If you would like a fast overview of Marshall’s significance, I recorded a short video on him for my Historical past of Financial Thought class some time again that you could be discover helpful. And if you wish to discover his seminal work Principles of Economics, it’s all obtainable for you at Econlib.
One of the vital vital contributions Marshall made to financial concept was his conceptualization of time. Time will not be a chronological phenomenon per se, however is relatively divided into classes relying on how folks can or can not change their consumption, manufacturing, funding, innovation, and institutional selections. His mannequin supplies a foundational framework for understanding how provide and demand reply to adjustments over completely different time horizons. He used the fishing trade for instance these time scales, displaying how producers’ skills to answer adjustments in demand evolve over completely different durations.
Marshall introduces three distinct time scales: the quick run, the quick run, and the long term.
- Quick Run: Within the quick run, provide is fastened and can’t reply to adjustments in demand. This era is so quick that no changes in manufacturing might be made. Costs might fluctuate considerably attributable to demand adjustments, however the amount equipped stays fixed. Marshall’s use of a day’s catch within the fishing trade illustrates this idea. Fishers can promote solely the fish they’ve already caught, and no further boats or nets might be deployed on such quick discover.
- Brief Run: Within the quick run, provide is considerably elastic however nonetheless constrained by present capability and sources. Producers can alter their output to a restricted extent through the use of present belongings extra intensively, similar to working longer hours or using extra labor. However they’ll’t but make important capital investments or adjustments to their manufacturing strategies. This response may contain fishers utilizing their boats extra ceaselessly or using extra crew members, however they nonetheless can not construct new boats or increase their fleet instantly.
- Lengthy Run: In the long term, provide turns into extremely elastic as producers can alter their manufacturing capability absolutely. This era permits for important investments in new capital, expertise, and infrastructure. Within the fishing trade, responses may embrace constructing extra boats, buying higher gear, and enhancing strategies, thereby rising the general catch. Over the long term, the market can attain a brand new equilibrium the place provide meets the altered demand at a extra secure value.
In Marshall’s summary mannequin this adjustment course of is easy and frictionless, though he was a relentless empiricist so he acknowledged inevitable frictions. Let’s apply this common mannequin to the present scenario with information heart electrical energy use and analyze the information laid out above.
Brief-Run Dynamics: Inelastic Provide and Quick Responses
Within the quick run, the provide of electrical energy is comparatively inelastic. Because of this the amount of electrical energy that may be generated and equipped to the market can’t be adjusted shortly in response to adjustments in demand. This inelasticity is as a result of important time and capital funding required to construct new energy vegetation or improve present infrastructure. So when information facilities improve exercise or new ones come on-line, electrical energy suppliers might battle to fulfill this demand with out resorting to expensive measures similar to buying energy from different areas or utilizing much less environment friendly peaking energy vegetation. This battle additionally has coverage implications, as we are going to see in future posts, as a result of closely-regulated nature of the electrical energy trade and its century-old enterprise mannequin. Observe particularly the big timing mismatch between information heart capability enlargement and electrical energy infrastructure capability enlargement.
Marshall’s dialogue of time in economics supplies a helpful analogy. Simply as fishermen can not immediately improve their catch in response to rising fish costs as a result of time required to construct extra boats and nets, electrical energy suppliers can not instantly ramp up manufacturing in response to elevated demand from information facilities. In each circumstances, the quick run is characterised by a set provide and value fluctuations pushed by demand adjustments.
Additionally, the environmental affect of counting on peaking energy vegetation, which frequently use fossil fuels, might be important, contributing to greater carbon emissions and undermining efforts to transition to cleaner power sources. These impacts are a subject for a future publish.
Lengthy-Run Changes: Funding and Capability Growth
The long term scenario differs significantly. Over time, the availability of electrical energy turns into extra elastic as new era capability is added and present infrastructure is upgraded. This long-run elasticity is pushed by funding in new energy vegetation, renewable power tasks, and developments in power storage expertise. Information heart operators and electrical energy suppliers can plan for and reply to anticipated will increase in demand by investing in capability enlargement.
Marshall’s framework helps us perceive this transition. In the long term, fishers can construct extra boats and enhance their fishing strategies, thereby rising their catch and stabilizing costs. Equally, within the electrical energy market, long-run changes contain substantial capital funding and technological innovation, resulting in a extra elastic provide curve and a extra secure equilibrium between provide and demand.
The funding in new era capability to fulfill the rising power calls for of knowledge facilities is already evident. For instance, many information heart operators are coming into into energy buy agreements (PPAs) with renewable power suppliers to safe a secure and sustainable power provide. These agreements not solely guarantee a gradual circulation of electrical energy but in addition promote the event of wind, photo voltaic, and different tasks like storage and geothermal. Developments in battery storage expertise allow information facilities to retailer extra power generated in periods of low demand and use it throughout peak durations, smoothing out fluctuations in electrical energy consumption.
Not like Marshall’s stylized fishing instance, these long-run changes in electrical energy take a very long time, longer than they may, due to many frictions that decelerate or forestall such versatile changes. Allowing forms and delays add years to infrastructure tasks, with doubtful or nonexistent advantages to these delays. The identical holds for grid operator interconnection, lengthy delays with unclear commensurate advantages. Allowing and interconnection are brakes on long-run provide adjustment that might in any other case be extra fluid. Supply chain problems are additionally an adjustment problem, such because the bottleneck that transformer provide presents for infrastructure enlargement tasks. That bottleneck itself supplies an instance illustrating Marshall’s level:
Moreover, the surge in demand for electrical gear might solely final for a couple of years, which makes suppliers hesitant to put money into larger provide capabilities that might end in over-supply circumstances when demand eases. This phenomenon mirrors previous experiences in markets like semiconductors, the place short-term market booms led to elevated capability, solely to face challenges when the market dynamics shifted. (Wooden Mackenzie 2024)
The Position of Technological Innovation
Technological innovation will play a vital position in shaping the long-run dynamics of knowledge heart power use and electrical energy demand. Improvements in information heart design, cooling applied sciences, and power effectivity measures can scale back the quantity of electrical energy consumed per unit of computing energy considerably. One vital instance is how the shift from conventional air cooling to liquid cooling techniques has improved power effectivity by lowering the necessity for air con (additionally the subject of a future publish). Algorithms to optimize server workloads and reduce idle occasions may also improve power effectivity.
Different manufacturing course of adjustments, such because the transition to extra energy-efficient {hardware} like superior processors and reminiscence modules designed to eat much less energy, are serving to information facilities scale back their total power footprint. These technological developments will decrease working prices for information heart operators and mitigate the affect on the electrical energy grid, making it simpler to accommodate the rising demand for AI and different digital providers. However even these within-firm capital investments take time.
The Position of Markets and Worth Alerts
One of many important challenges within the electrical energy trade is the shortage of efficient market alerts and value mechanisms to point relative shortage and handle demand. In a extra versatile and responsive market, costs would rise when electrical energy is scarce and fall when it’s plentiful, signaling to each producers and customers to regulate their habits accordingly. Implementing such value alerts may result in larger flexibility and effectivity within the electrical energy market.
For instance, real-time pricing or time-of-use pricing could possibly be launched to replicate the precise price of electrical energy manufacturing and provide at completely different occasions of the day. Beneath real-time pricing, electrical energy costs would fluctuate based mostly on present provide and demand circumstances, encouraging customers to shift their utilization to off-peak occasions when costs are decrease. Information facilities that may schedule non-urgent computational duties may benefit from decrease costs in periods of low demand, lowering their total power prices and assuaging stress on the grid throughout peak occasions. Given their substantial and sometimes versatile power consumption, information facilities are additionally good candidates for bulk-scale demand response providers provided by corporations like Voltus and CPower. By quickly cutting down operations or shifting workloads to off-peak durations, information facilities can assist steadiness provide and demand, stabilize costs, and scale back the necessity for costly and emissions-heavy peaking energy vegetation.
However the regulatory and market establishments must allow such markets and value alerts to scale back frictions that preserve the timing mismatch between demand development and rising provide. They don’t. Whereas some demand response integration exists in wholesale energy markets it’s restricted and closely constrained. That constraint, alongside the frictions of allowing and interconnection that act as brakes conserving provide extra inelastic than it may in any other case be, present that we nonetheless have so much to study from Marshall’s mannequin of time.
Electrons are like fish as a result of catching them requires constructing stuff. Constructing stuff is expensive and takes time, rather more so within the case of electrons than of fish attributable to regulatory impediments which are frictions that amplify the timing mismatches within the adjustment of each demand and provide.
This publish initially appeared on Lynne’s Substack, The Data Drawback. Please contemplate subscribing here.