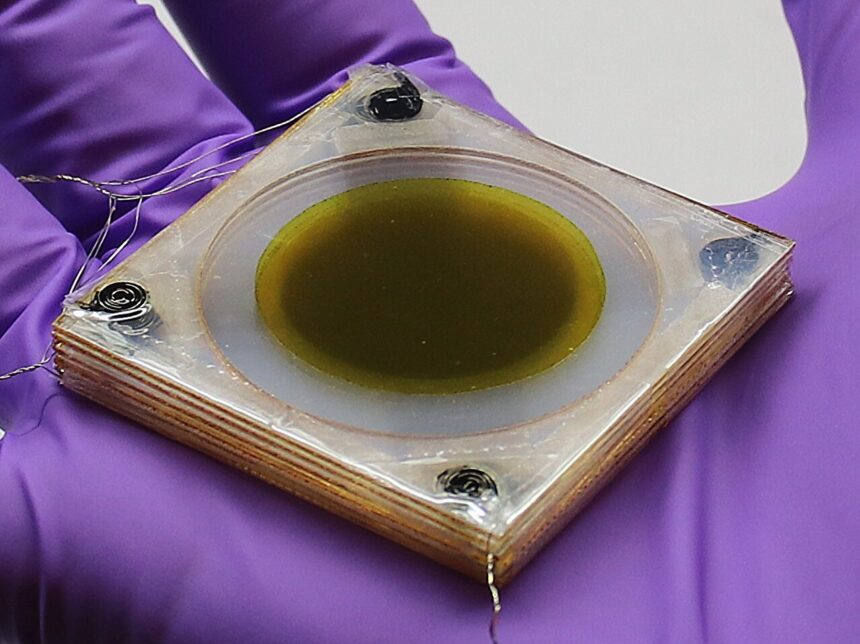
UCLA supplies scientists have developed a compact cooling expertise that may pump away warmth constantly utilizing layers of flexing skinny movies. The design relies on the electrocaloric impact, wherein an electrical area causes a brief change in a cloth’s temperature.
In lab experiments, the researchers discovered that the prototype may decrease ambient temperatures of its rapid environment by 16 levels Fahrenheit constantly and as much as 25 levels on the supply of the warmth after about 30 seconds.
Detailed in a paper published within the journal Science, the method might be integrated into wearable cooling expertise or moveable cooling units.
“Our long-term purpose is to develop this expertise for wearable cooling equipment which might be snug, reasonably priced, dependable and energy-efficient—particularly for individuals who work in extremely popular environments over lengthy hours,” mentioned principal investigator Qibing Pei, a professor of supplies science and engineering on the UCLA Samueli College of Engineering. “As common temperatures proceed to rise with local weather change, dealing with warmth is turning into a vital well being concern. We want a wide range of options to the issue and this might be the premise for one.”
The experimental materials consists of a round stack of six skinny polymer movies, just below an inch in diameter and one-quarter of an inch thick for the complete stack. Every layer is coated with carbon nanotubes on each side. The ensuing materials is ferroelectric, which suggests it modifications form when an electrical area is utilized.
When the gadget’s electrical area is switched on, the stacked layers compress towards one another in pairs. When the electrical energy switches off, the stacked pairs come aside to then press towards the opposite neighboring layers. As this alternating course of repeats itself, the self-regenerative, accordion-like cascading motion frequently pumps warmth away, layer by layer.
“The polymer movies use a circuit to shuttle fees between pairs of stacked layers, which makes the versatile cooling gadget extra environment friendly than air conditioners,” mentioned Hanxiang Wu, one of many research’s co-lead authors and a postdoctoral scholar working in Pei’s lab.

Conventional cooling expertise depends on air con and refrigeration, which require vapor compression that not solely consumes a substantial amount of vitality but additionally makes use of carbon dioxide as a coolant. The brand new gadget is an easier design that doesn’t require greenhouse-gas-generating coolants or liquids. It operates solely with electrical energy, which might be sustainable when generated by way of renewable vitality sources corresponding to photo voltaic panels.
“This cooling gadget integrates superior supplies with a sublime mechanical structure to ship energy-efficient cooling by embedding performance immediately into its construction, lowering complexity, vitality use and computational calls for,” mentioned the research’s co-lead writer Wenzhong Yan, a postdoctoral scholar in mechanical engineering.
Pei holds a joint school appointment within the Division of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering and runs the Delicate Supplies Analysis Laboratory at UCLA. He and his group have been researching electrocaloric cooling applied sciences designed to drop sufficient temperatures for real-world purposes.
“As a result of we are able to use skinny versatile movies, electrocaloric cooling can be most supreme for next-generation wearables that may hold us cool underneath strenuous situations,” Pei mentioned. “It is also used to chill electronics with versatile parts.”
Sumanjeet Kaur, a supplies employees scientist at Lawrence Berkeley Nationwide Laboratory and chief of its Thermal Power Group, is one other writer of the research and a co-inventor on the patent utility UCLA has filed for this invention. “The potential of environment friendly wearable cooling in driving vitality financial savings and mitigating local weather change can’t be overstated,” Kaur mentioned.
Along with Wu and Yan, Yuan Zhu, a UCLA Samueli graduate scholar and member of Pei’s analysis group, is one other co-lead writer. Different authors are supplies science graduate college students Siyu Zhang, William Budiman, Kede Liu, Jianghan Wu and former supplies science postdoctoral scholar Yuan Meng—all members of Pei’s analysis group; bioengineering graduate scholar Xun Zhao; and Ankur Mehta, a UCLA affiliate professor {of electrical} and laptop engineering.
Extra data:
Hanxiang Wu et al, A self-regenerative warmth pump based mostly on a dual-functional relaxor ferroelectric polymer, Science (2024). DOI: 10.1126/science.adr2268
Quotation:
Subsequent-generation wearables: Compact cooling pump drops temperatures by 16°F (2025, January 14)
retrieved 19 January 2025
from https://techxplore.com/information/2025-01-generation-wearables-compact-cooling-temperatures.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.