In February 2024, the disruption of three submarine communications cables within the Purple Sea highlighted the continued issues over the vulnerability of the world’s fragile knowledge networking connections.
The anchor of a cargo ship that was attacked by Houthi militants was deemed to be the most definitely trigger of harm to the Seacom, TGN, AAE-1, and EIG cables, which play an important function in connecting Europe and Asia’s infrastructure.
As soon as lower, a submarine cable can take months to restore. If widespread sabotage had been to happen, disruptions might span months, underlining subsea cables as a persistent weak hyperlink within the integrity of worldwide digital infrastructure, in line with specialists.
“Subsea cable breaks are unusual, however after they do occur restore occasions will be prolonged. It may take wherever from six weeks to 6 months to get permits and a restore ship in place and begin the repair,” Andy Fortress, vice chairman of digital interconnection operations and engineering at Equinix, advised DCN.
As these vulnerabilities come to gentle, the necessity for a strong framework to safe subsea cable infrastructure has by no means been extra vital. With a restricted variety of vessels tasked with the upkeep and safety of those important communications hyperlinks, the challenges of safeguarding such an enormous digital panorama have gotten more and more obvious.
The Gathering Storm: Defending the International Internet of Subsea Cables
Subsea cable upkeep is roofed by non-profit cooperative agreements and arranged through world zones. Europe is roofed by the Atlantic Cable Upkeep & Restore Settlement (ACMA), and the Mediterranean Cable Upkeep Settlement (MECMA), which covers the Mediterranean Sea, the Black Sea, and the Purple Sea.
Regardless of the huge geographic space they cowl, a report (PDF) compiled for the European Parliament in 2022 signifies that simply 4 ships are accountable for sustaining cables from the Atlantic to the Purple Sea – three primarily based within the European Union and one primarily based within the UK. Globally, there are simply 22 vessels geared up with the mandatory specialist gear.
Simply 4 boats preserve subsea cables throughout the Atlantic and the Purple Sea (Picture: Alamy)
The European Union report was printed in June 2022, simply three months earlier than the destruction of the Nord Stream gas pipeline, which piped pure gasoline from Russia to Germany.
A 12 months later, following information of the German police investigation, former Russian president Dmitry Medvedev, at present deputy chairman of the Safety Council of the Russian Federation, used his Telegram channel to subject an express risk to submarine communications cables, claiming that Russia had a “proper” to assault them in retaliation.
Indications of state-sponsored curiosity in world submarine communication cables are nothing new. The EU safety report was commissioned following years of more and more suspicious nation-state exercise round submarine communications cables – particularly by vessels formally or unofficially linked with the states of Russia and China.
“We are actually seeing Russian underwater exercise within the neighborhood of undersea cables that I don’t imagine we’ve ever seen [before],” US Navy Rear Admiral Andrew Lennon, commander of NATO’s submarine forces, told The Washington Post in 2017. “Russia is clearly taking an curiosity in… NATO nations’ undersea infrastructure,” he added.
5 years later, Royal Navy admiral Sir Tony Radakin, head of the UK’s armed forces, noted a “phenomenal improve in Russian submarine and underwater exercise” because the flip of the century, culminating in live-fire exercises off the coast of Ireland in January 2022 by the Russian Navy. Their chosen location was within the neighborhood of a number of submarine communications cables linking the UK, France, and the US.
China’s function within the world subsea cable market is extra advanced. HMN Applied sciences is among the greatest world gamers within the submarine cable laying and restore market. Furthermore, funding in cable infrastructure can also be a key part of the Chinese language authorities’s Digital Silk Highway challenge.
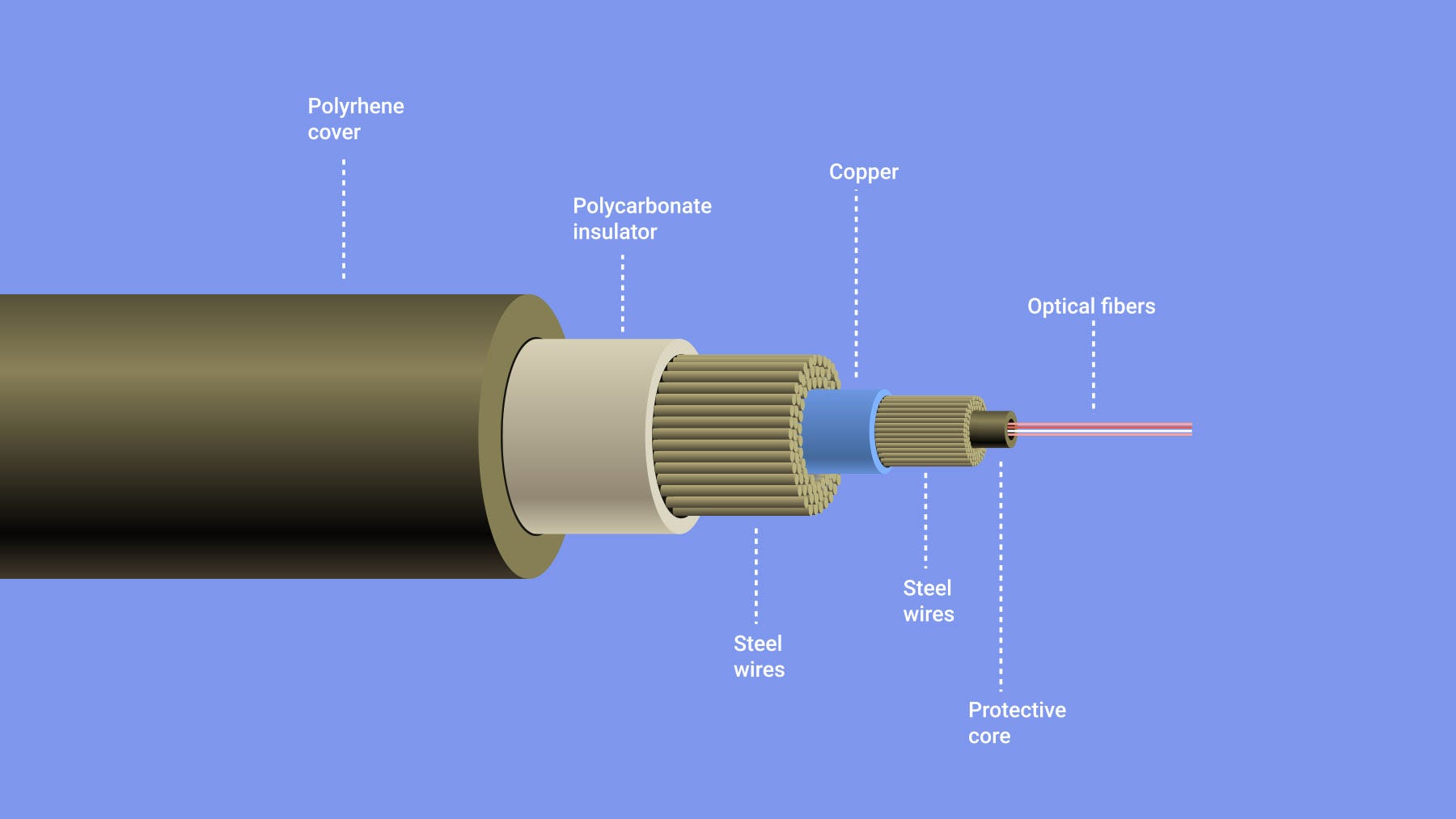
A simplified cross-section of a subsea fiber optic cable (Picture: Alamy)
On the identical time, nonetheless, China’s assertive international coverage has seen it concerned in incursions into land, waters, and airspace belonging to Taiwan, Japan, the Philippines, Malaysia, Vietnam, India, and Bhutan in recent times.
Furthermore, China claims the entire of the South China Sea as its personal. This has a singular set of implications for submarine communication cables traversing the area, in addition to cables connecting to Taiwan.
Learn extra of the newest knowledge heart networking information
Round Africa, in the meantime, the image is considerably blurred. Denys Reva, a researcher for the Institute for Safety Research in Pretoria, South Africa, advised DCN: “Europe has a really well-developed maritime area consciousness system, the place they’re cognizant of which ships are transferring and the place they’re transferring, however that is a lot much less well-developed in Africa, though it does range from nation to nation,”
In consequence, probably nefarious subsea cable exercise isn’t monitored practically as carefully round Africa as it’s in European waters.
The potential risk is compounded by comparatively poor land-based connections between nations in Africa, added Reva. On the upside, Cape City supplies a base for one of many world’s handful of submarine cable restore ships.
Put on, Tear, and Pure Disasters
Whereas assaults from nation-states loom massive, the vast majority of submarine cable harm happens by chance – from careless dredgers to pure disasters.
Certainly, the most important hazard comes from earthquakes, tsunamis, and highly effective underwater currents. The undercurrents off the coast of Africa by the estuary of the Congo River are significantly difficult for subsea cable infrastructure, says Reva.
Earthquakes, in the meantime, will be simply as damaging as sunken ships. When the Tōhoku seaquake occurred in 2011 it induced the rupture of 4 of the 20 submarine cables connecting Japan.
Nevertheless, there’s no denying that nefarious dangers are growing.
NATO has responded by re-establishing Chilly Battle-era maritime capabilities, together with the procurement of maritime patrol plane and ships, and a brand new North Atlantic Command to coordinate NATO exercise to fight the risk.
The digital infrastructure business, too, has responded with embedded SMART – science monitoring and dependable telecommunications – cable know-how able to capturing real-time environmental info.

SMART cables add sensor elements to business subsea fiber optic cables that acquire seismic and oceanographic knowledge (Picture: Sub Sea Knowledge Methods)
In line with Fortress: “These sensors are used to seize real-time monitoring of water temperature, water strain, and examine motion of tectonic plates. This may present vital warnings to inhabitants facilities after they detect tsunamis & earthquakes, serving to with alert methods and emergency preparedness.”
SMART cable deployments have gained momentum in recent times, regardless of excessive prices.
Fortress at Equinix mentioned there’s a rising choice of potential technical options to assist shield underwater community cables. “There are a number of proactive measures that may be taken to guard subsea cables and terrestrial fiber infrastructure,” he mentioned. “Designing and deploying networks from the start to deal with resiliency, redundancy, and attain is a large begin.
“Issues like elevated energetic sensor monitoring, including extra receiving stations for Alarm Identification Methods (AIS), and energetic fiber monitoring to sectionalize faults as much as 200km. But additionally selling training and cable consciousness and safety applications to maritime communities, fishermen, and ports in areas all over the world with subsea cable infrastructure.”
These will all assist, in fact, nevertheless it stays to be seen how a lot they may assist in the face of decided, coordinated, and well-resourced attackers.




