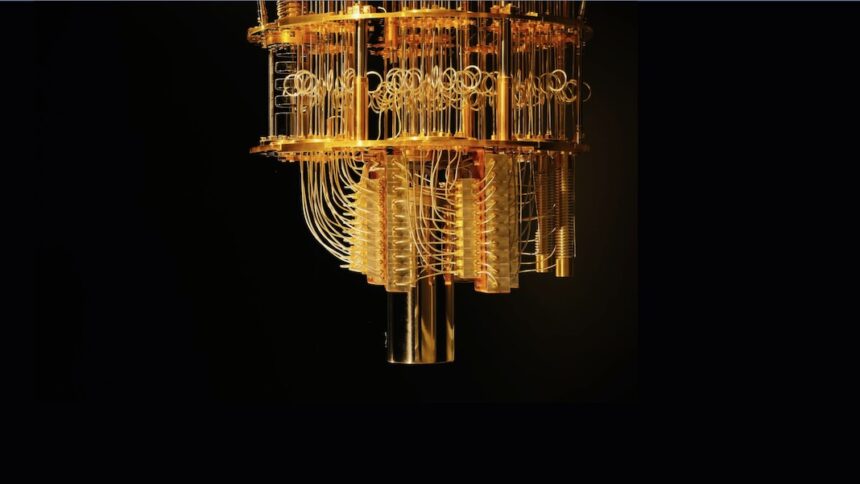
In June, an IBM computing executive claimed quantum computers were entering the “utility” phase, in which high-tech experimental devices become useful. In September, Australia’s chief scientist Cathy Foley went so far as to declare “the dawn of the quantum era.”
This week, Australian physicist Michelle Simmons won the nation’s top science award for her work on developing silicon-based quantum computers.
Obviously, quantum computers are having a moment. But—to step back a little—what exactly are they?
What Is a Quantum Computer?
One way to think about computers is in terms of the kinds of numbers they work with.
The digital computers we use every day rely on whole numbers (or integers), representing information as strings of zeroes and ones which they rearrange according to complicated rules. There are also analog computers, which represent information as continuously varying numbers (or real numbers), manipulated via electrical circuits or spinning rotors or moving fluids.
In the 16th century, the Italian mathematician Girolamo Cardano invented another kind of number called complex numbers to solve seemingly impossible tasks such as finding the square root of a negative number. In the 20th century, with the advent of quantum physics, it turned out complex numbers also naturally describe the fine details of light and matter.
In the 1990s, physics and computer science collided when it was discovered that some problems could be solved much faster with algorithms that work directly with complex numbers as encoded in quantum physics.
The next logical step was to build devices that work with light and matter to do those calculations for us automatically. This was the birth of quantum computing.
Why Does Quantum Computing Matter?
We usually think of the things our computers do in terms that mean something to us— balance my spreadsheet, transmit my live video, find my ride to the airport. However, all of these are ultimately computational problems, phrased in mathematical language.
As quantum computing is still a nascent field, most of the problems we know quantum computers will solve are phrased in abstract mathematics. Some of these will have “real world” applications we can’t yet foresee, but others will find a more immediate impact.
One early application will be cryptography. Quantum computers will be able to crack today’s internet encryption algorithms, so we will need quantum-resistant cryptographic technology. Provably secure cryptography and a fully quantum internet would use quantum computing technology.
In materials science, quantum computers will be able to simulate molecular structures at the atomic scale, making it faster and easier to discover new and interesting materials. This may have significant applications in batteries, pharmaceuticals, fertilizers, and other chemistry-based domains.
Quantum computers will also speed up many difficult optimization problems, where we want to find the “best” way to do something. This will allow us to tackle larger-scale problems in areas such as logistics, finance, and weather forecasting.
Machine learning is another area where quantum computers may accelerate progress. This could happen indirectly, by speeding up subroutines in digital computers, or directly if quantum computers can be reimagined as learning machines.
What Is the Current Landscape?
In 2023, quantum computing is moving out of the basement laboratories of university physics departments and into industrial research and development facilities. The move is backed by the checkbooks of multinational corporations and venture capitalists.
Contemporary quantum computing prototypes—built by IBM, Google, IonQ, Rigetti, and others—are still some way from perfection.
Today’s machines are of modest size and susceptible to errors, in what has been called the “noisy intermediate-scale quantum” phase of development. The delicate nature of tiny quantum systems means they are prone to many sources of error, and correcting these errors is a major technical hurdle.
The holy grail is a large-scale quantum computer which can correct its own errors. A whole ecosystem of research factions and commercial enterprises are pursuing this goal via diverse technological approaches.
Superconductors, Ions, Silicon, Photons
The current leading approach uses loops of electric current inside superconducting circuits to store and manipulate information. This is the technology adopted by Google, IBM, Rigetti, and others.
Another method, the “trapped ion” technology, works with groups of electrically charged atomic particles, using the inherent stability of the particles to reduce errors. This approach has been spearheaded by IonQ and Honeywell.
A third route of exploration is to confine electrons within tiny particles of semiconductor material, which could then be melded into the well-established silicon technology of classical computing. Silicon Quantum Computing is pursuing this angle.
Yet another direction is to use individual particles of light (photons), which can be manipulated with high fidelity. A company called PsiQuantum is designing intricate “guided light” circuits to perform quantum computations.
There is no clear winner yet from among these technologies, and it may well be a hybrid approach that ultimately prevails.
Where Will the Quantum Future Take Us?
Attempting to forecast the future of quantum computing today is akin to predicting flying cars and ending up with cameras in our phones instead. Nevertheless, there are a few milestones that many researchers would agree are likely to be reached in the next decade.
Better error correction is a big one. We expect to see a transition from the era of noisy devices to small devices that can sustain computation through active error correction.
Another is the advent of post-quantum cryptography. This means the establishment and adoption of cryptographic standards that can’t easily be broken by quantum computers.
Commercial spin-offs of technology such as quantum sensing are also on the horizon.
The demonstration of a genuine “quantum advantage” will also be a likely development. This means a compelling application where a quantum device is unarguably superior to the digital alternative.
And a stretch goal for the coming decade is the creation of a large-scale quantum computer free of errors (with active error correction).
When this has been achieved, we can be confident the 21st century will be the “quantum era.”
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Image Credit: A complex cooling rig is needed to maintain the ultracold working temperatures required by a superconducting quantum computer / IBM