Tim Doiron, VP Answer Advertising and marketing at Infinera, explores why managed optical fiber networks could possibly be the important thing to powering right this moment’s bandwidth-hungry knowledge centre growth.
Managed optical fiber networks (MOFNs) play an more and more essential function for communication service suppliers (CSPs) in assembly the bandwidth calls for of web content material suppliers (ICPs).
The increasing deployment of power-hungry GPUs that underpin AI with purposes like ChatGPT and Copilot has sparked a world knowledge centre building growth, with the variety of knowledge centres anticipated to double within the subsequent few years.
However knowledge facilities don’t exist in isolation. They’re linked by way of high-speed optical connectivity to different knowledge centres and web change areas, enabling geographical redundancy whereas additionally sharing workloads, storage, and more and more, responding to generative AI queries. So, what’s a MOFN, how does it differ from a conventional optical networking method, and why is it taking place?
Conventional managed bandwidth
To know MOFNs, let’s first evaluation conventional optical transport networks and repair supply.
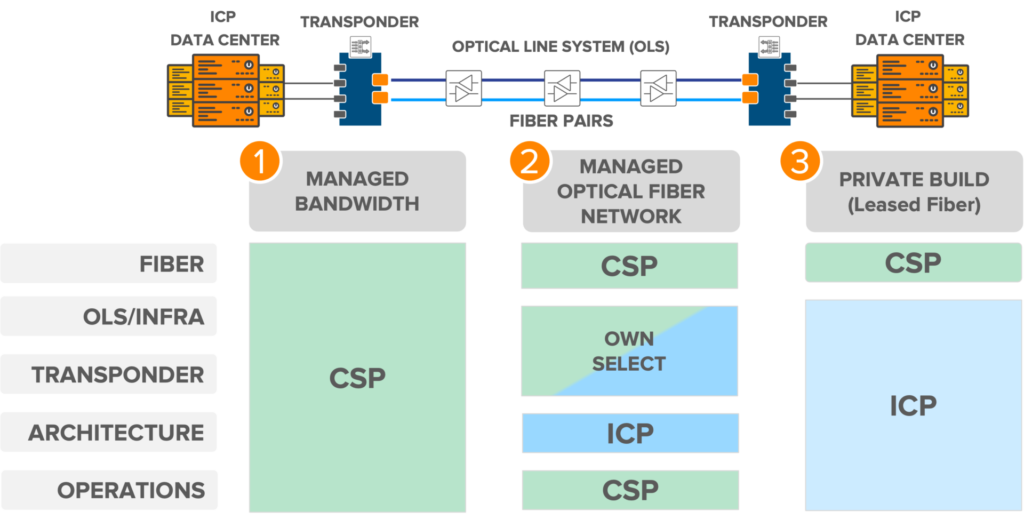
As depicted in Determine 1, a CSP invests in trenching optical fibres and installs optical line system tools to allow wavelengths to ingress and egress the fibre and coherent optical engines to gentle the fibre – like right this moment’s 1.2+ Tb/s-per-wavelength transponder sleds or 800 Gb/s multi-haul coherent pluggables. The CSP then presents transport companies over this shared infrastructure to any buyer that will want them, together with enterprises and ICPs.
For instance, one can lease one or a number of 100 Gb/s or 400 Gb/s transport companies throughout a metro, a continent, and even an ocean within the case of submarine networks. The enterprise or ICP pays a month-to-month recurring charge to the CSP for the capability of the transport service offered and the service-level settlement (SLA) related to the service.
Huge capability driving non-public builds
There are, nonetheless, cases the place an enterprise or ICP wants vital quantities of connectivity – say sufficient to eat the capability of 1 or a number of fibre pairs – delivering a number of tens of terabits per second. In such cases, the enterprise or ICP could select to construct and handle its personal non-public optical transport community. This often includes leasing darkish fibre from a CSP like Arelion, Exa, Lumen Zayo, or different darkish fibre wholesale supplier. The enterprise or ICP then assumes the duty for buying, putting in, and managing the optical line system and optical engine tools. In brief, they tackle the duties of the service supplier for the dependable transport of their community visitors.
Carry on the MOFNs
That brings us to MOFNs. As additionally depicted in Determine 1, a MOFN sits architecturally and commercially between the standard managed bandwidth method and the darkish fibre private-build method.
MOFNs contain high-capacity networks and the shut collaboration of a CSP, an ICP, and an optical vendor with intensive ICP and knowledge centre interconnect expertise and know-how.
The first driver for MOFNs is the rising variety of knowledge centres and the necessity for high-speed interconnectivity amongst them. Whereas knowledge centre development is a world phenomenon, we see explicit acceleration in India and all through Asia, the Center East, and elements of Africa.
With greater than 90 new submarine cables deliberate for deployment globally within the subsequent few years, MOFNs additionally play a key function within the backhaul portion of submarine networks – connecting submarine cable touchdown station visitors to knowledge centres which may be lots of and even hundreds of kilometers away.
But when ICPs want high-capacity connectivity amongst knowledge centres, why don’t they simply gentle up darkish fibre and create a non-public community? There are three key causes: 1) regulation, 2) assets, and three) threat.
In some geographies, corresponding to India, regulatory necessities could stop ICPs from performing as a transport community operator. In different circumstances, an ICP could lack the correct assets or certified optical networking personnel to tackle the added duty of working an optical transport community. Moreover, an ICP could also be coming into a brand new market or a brand new nation and should need to scale back its threat by leveraging the abilities, expertise, and relationships of an in-country incumbent service supplier. However the ICP would nonetheless need to affect the community design, and the kind of optical tools deployed.
Proper capability, proper structure, proper answer
With MOFNs, the ICP directs the community structure and vendor preferences for the optical line system and optical engine know-how. With new knowledge centre building, it’s essential that server, storage, and compute tools be put in and activated at simply the correct time.
It’s equally essential that knowledge centre interconnect capability is delivered proper on time for the information centre to go dwell. Given the extremely engaged three-way relationship amongst ICP, CSP, and distributors in MOFNs, the profit for the ICP is that it receives the correct capability from its most popular DCI vendor when and the place it’s wanted, and at an financial worth that meets its enterprise goals. The CSP in flip utilises its networking abilities and experience to develop its ICP enterprise with a dependable recurring income stream whereas leveraging the most recent DCI vendor options.
Whereas now we have handled MOFNs as one measurement matches all, it’s price noting that MOFNs do come in numerous styles and sizes relying upon the community and the individuals. Along with what is printed in Determine 1, there are variations to this mannequin together with a hybrid method the place the CSP builds a devoted optical line system and the ICP deploys its personal optical engine know-how excessive.
In all MOFN circumstances, an ICP, CSP, and main DCI vendor collaborate to satisfy the ICP’s architectural, know-how, and enterprise goals.
Wrapping up MOFNs
MOFNs characterize a big evolution in the way in which ICPs and CSPs collaborate to satisfy the rising calls for for high-capacity optical transport. As knowledge centres proceed to proliferate globally, pushed by the growing deployment of AI purposes and the necessity for geographical redundancy, MOFNs supply a versatile and environment friendly answer.
By leveraging the experience of CSPs and the technological developments of optical distributors, ICPs can obtain the correct capability, structure, and financial worth to help their enterprise goals. This collaborative method not solely ensures well timed and dependable connectivity but additionally mitigates the dangers related to non-public community builds.
Because the digital panorama continues to evolve, MOFNs will play a vital function in enabling seamless and scalable connectivity for the longer term.




