Safety Operations Facilities function the vigilant defenders of organizations, defending them towards evolving cyberattacks. Whereas their operations and instruments could seem arcane to these unfamiliar with the sector, understanding their core features is essential.
This text goals to demystify the important instruments that Safety Operations Facilities (SOCs) – and safety organizations usually – rely upon to stop and fight cyberattacks. By addressing each vulnerability and incident management, we discover how these twin elements work collectively to fortify organizational defenses.
Determine 1: Perceive the goals and instruments for safety organizations.
Stopping Safety Incidents
CISOs and CIOs are in massive bother if they’re unprepared for cyberattacks. Dashing to repair a whole bunch of servers on the final minute is usually futile. The fact is straightforward: Organizations have to be safe earlier than an assault happens, making day by day vulnerability administration a necessity.
Securing the Growth Pipeline
For in-house software program improvement, it’s essential to embed static and dynamic software safety testing (SAST/DAST) instruments like SonarQube and Veracode into CI/CD pipelines, complemented by periodic penetration exams. Nevertheless, vulnerabilities usually floor post-deployment, as seen with the Log4j incident. When the horrific flaw emerged, organizations scrambled to evaluate dangers and implement fixes – a large effort that may’t be sustained frequently.
To handle vulnerabilities at scale, CISOs can undertake complementary approaches:
-
Steady Monitoring of Deployed Artifacts. Instruments like Google Cloud Platform’s Artifact Registry scan repositories for newly found vulnerabilities. Standardized deployment processes guarantee all parts are accounted for, however challenges come up with decommissioned artifacts triggering false alarms.
-
Runtime Setting Monitoring. Monitoring in runtime environments avoids false positives from previous artifacts now not in use. Nevertheless, figuring out all runtime environments (e.g., in a PaaS context) will be complicated.
-
Automated Penetration Testing. Providers like GCP Net Safety Scanner periodically test for exploitable net software points. Whereas much less thorough than handbook checks, they supply constant protection for widespread vulnerabilities.
Hardening Infrastructure and Cloud Administration
Past software program, runtime environments introduce Docker platform and OS vulnerabilities. Lacking patches are a significant concern, however the (almost excellent) homogeneity of Home windows and Linux VMs and mature merchandise like Azure Replace Supervisor simplify patch administration by detecting outdated patches and automating updates at scale.
VM misconfigurations, equivalent to open RDP ports or improper IAM setups, pose one other threat, particularly in cloud environments. Challenges lengthen to PaaS companies like cloud features or database companies, the place misconfigurations can result in extreme safety gaps.
Whereas cloud suppliers are chargeable for guaranteeing patched and safe companies, prospects should correctly configure cloud parts like IAM roles or S3 buckets. To handle cloud safety successfully, CISOs can deploy cloud-native instruments, equivalent to AWS Guard Obligation, Microsoft Defender, and third-party merchandise like Prisma, to evaluate and enhance the general safety posture.
Orchestrating Vulnerability Remediation
Efficient vulnerability administration requires sturdy workflows. Some important processes are assigning vulnerabilities to the correct engineers, eradicating resolved points from the to-do listing, and marking irrelevant vulnerabilities. Safety toolsets should combine workflow assist to make sure vulnerabilities are addressed successfully.
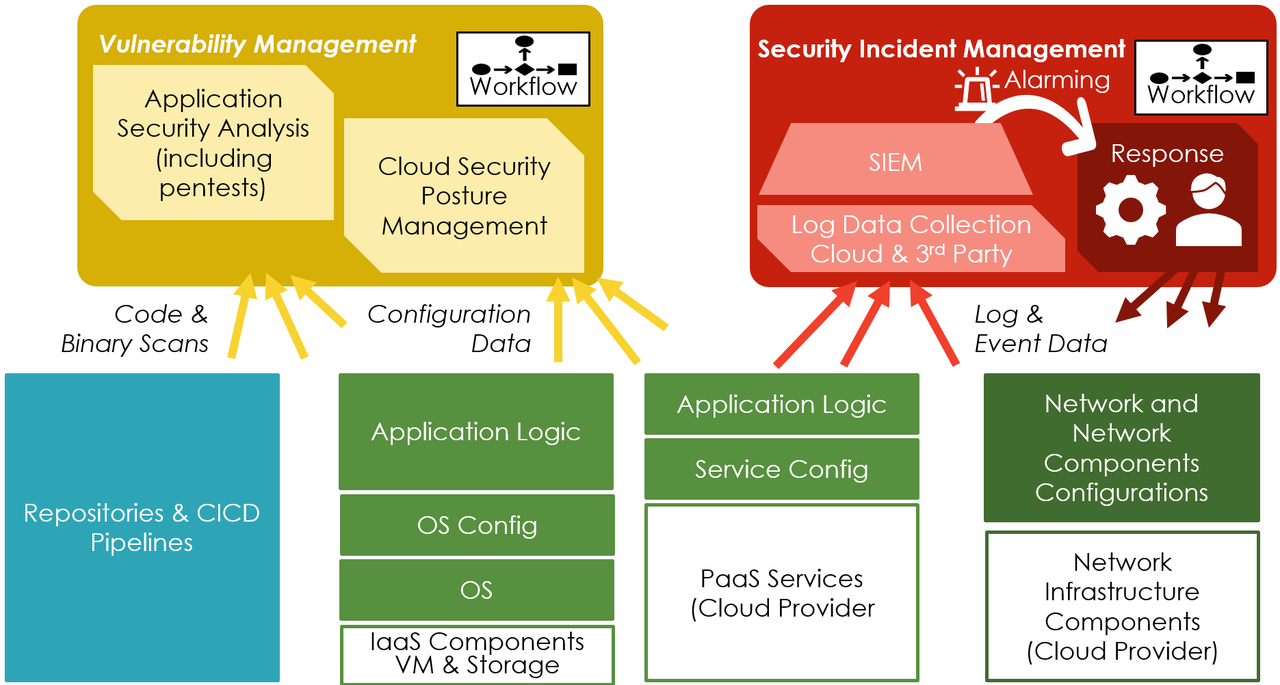
Determine 2: An architectural perspective of the instruments for safety operations facilities.
Incident Detection and Response
Whereas vulnerability administration reduces the danger of assaults, most organizations will finally face an intrusion.
A typical instance is malware infecting VMs, which attackers would possibly use for crypto-mining or denial-of-service assaults. Detecting such incidents usually begins with malware scanning utilizing cloud-native or third-party instruments. Redeploying a clear OS picture and reinstalling software program can resolve the difficulty, offered the attackers haven’t put in backdoors or created accounts.
Nevertheless, malware scanning focuses narrowly on binaries. Superior safety methods incorporate behavioral analytics to detect suspicious actions, equivalent to a VM connecting to a identified cybercriminal IP or a person logging in from geographically distant places inside minutes. The strategies depend on log information, which clouds present extensively. The problem is choosing the proper logs to activate with out exploding storage prices.
Position of SIEM Methods
Safety Info and Occasion Administration (SIEM) methods are essential for correlating occasions throughout logs, enriching logs with exterior intelligence (e.g., identified malicious IPs), and figuring out delicate assault indicators. SIEMs are strategic property that combine information from the cloud, on-premises environments, IoT units, and enterprise endpoints like laptops and tablets.
Structured Processes and SOAR Instruments
Incident detection and response require structured processes involving incident handlers, safety analysts, software program engineers, admins, and exterior companions. Enterprise-level course of administration instruments like Jira or ITSM are needed for coordination, as primary alerting options (e.g., textual content messages) are inadequate for big organizations.
Rising SOAR (Safety Orchestration, Automation, and Response) instruments improve incident triage, information enrichment, and incident response via automation. For instance, playbook scripts can reduce web connectivity throughout large information outflow. Whereas such actions would possibly disrupt enterprise operations, even five-minute delays in response can enable attackers to exfiltrate vital information.
Challenges in Cloud Incident Response
Responding to classy assaults in cloud environments is extra complicated than endpoint detection and response (EDR) for laptops and VMs. EDR instruments can shortly isolate contaminated endpoints, however related capabilities for PaaS cloud companies don’t exist (but). SOC groups face a dilemma in understanding numerous cloud applied sciences and dependencies. Granting them admin rights for all cloud workloads introduces operational and safety dangers, particularly if attackers compromise these accounts. Organizations should discover methods to reply successfully regardless of gaps in instrument protection.
Unifying Prevention and Response
Vulnerability and incident administration are complementary pillars of safety. Incident administration focuses on logging, detecting uncommon occasions, and responding to assaults, whereas vulnerability administration reduces the danger floor via patching and configuration. Collectively, they’re important for holding attackers out or swiftly eradicating them.




