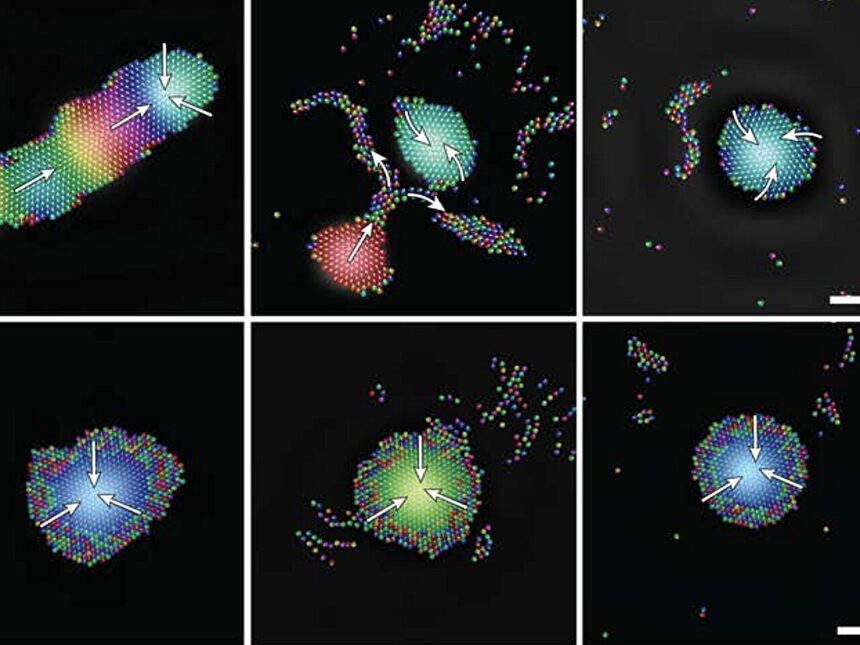
Animals like bats, whales and bugs have lengthy used acoustic indicators for communication and navigation. Now, a global group of scientists has taken a web page from nature’s playbook to mannequin micro-sized robots that use sound waves to coordinate into massive swarms that exhibit intelligent-like conduct.
The robotic teams may sooner or later perform complicated duties like exploring catastrophe zones, cleansing up air pollution, or performing medical remedies from contained in the physique, in response to group lead Igor Aronson, Huck Chair Professor of Biomedical Engineering, Chemistry, and Arithmetic at Penn State.
“Image swarms of bees or midges,” Aronson stated. “They transfer, that creates sound, and the sound retains them cohesive, many people performing as one.”
The researchers have published their work within the journal Bodily Evaluate X.
Because the miniature, sound-broadcasting swarms of micromachines are self-organizing, they’ll navigate tight areas and even re-form themselves if deformed. The swarms’ collective—or emergent—intelligence may sooner or later be harnessed to hold out duties like cleansing up air pollution in contaminated environments, Aronson defined.
Past the atmosphere, the robotic swarms may probably work contained in the physique, delivering medication on to an issue space, for instance. Their collective sensing additionally helps in detecting adjustments in environment, and their skill to “self-heal” means they’ll preserve functioning as a collective unit even after breaking up, which could possibly be particularly helpful for menace detection and sensor functions, Aronson stated.
“This represents a major leap towards creating smarter, extra resilient, and in the end extra helpful microrobots with minimal complexity that might deal with a few of our world’s hardest issues,” he stated. “The insights from this analysis are essential for designing the following technology of microrobots, able to performing complicated duties and responding to exterior cues in difficult environments.”
For the examine, the group developed a pc mannequin to trace the actions of tiny robots, every geared up with an acoustic emitter and a detector. They discovered that acoustic communication allowed the person robotic brokers to work collectively seamlessly, adapting their form and conduct to their atmosphere, very similar to a faculty of fish or a flock of birds.
Whereas the robots within the paper have been computational brokers inside a theoretical—or agent-based—mannequin, fairly than bodily gadgets that have been manufactured, the simulations noticed the emergence of collective intelligence that will probably seem in any experimental examine with the identical design, Aronson stated.
“We by no means anticipated our fashions to point out such a excessive degree of cohesion and intelligence from such easy robots,” Aronson stated. “These are quite simple digital circuits. Every robotic can transfer alongside in some course, has a motor, a tiny microphone, a speaker and an oscillator. That is it, however nonetheless it is able to collective intelligence. It synchronizes its personal oscillator to the frequency of the swarm’s acoustic discipline and migrates towards the strongest sign.”
The invention marks a brand new milestone for a budding discipline known as lively matter, the examine of the collective conduct of self-propelled microscopic organic and artificial brokers, from swarms of micro organism or residing cells to microrobots. It exhibits for the primary time that sound waves can perform as a method of controlling the micro-sized robots, Aronson defined. Up till now, lively matter particles have been managed predominantly by way of chemical signaling.
“Acoustic waves work significantly better for communication than chemical signaling,” Aronson stated. “Sound waves propagate sooner and farther virtually with out lack of power—and the design is way easier. The robots successfully ‘hear’ and ‘discover’ one another, resulting in collective self-organization. Every aspect may be very easy. The collective intelligence and performance come up from minimal elements and easy acoustic communication.”
The opposite authors on the paper are Alexander Ziepke, Ivan Maryshev and Erwin Frey of the Ludwig Maximilian College of Munich.
Extra data:
Alexander Ziepke et al, Acoustic Signaling Allows Collective Notion and Management in Lively Matter Techniques, Bodily Evaluate X (2025). DOI: 10.1103/m1hl-d18s
Quotation:
Tiny robots use sound to self-organize into clever teams (2025, August 12)
retrieved 12 August 2025
from https://techxplore.com/information/2025-08-tiny-robots-intelligent-groups.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.