Optical neural networks could present the high-speed and large-capacity answer essential to sort out difficult computing duties. Nevertheless, tapping their full potential would require additional advances. One problem is the reconfigurability of optical neural networks.
A analysis workforce within the Stiller Analysis Group on the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Gentle, in collaboration with the Englund Analysis Group on the Massachusetts Institute of Know-how, has now succeeded in laying the inspiration for brand new reconfigurable neuromorphic constructing blocks by including a brand new dimension to photonic machine studying: sound waves. Their findings are published in Nature Communications.
The researchers use mild to create short-term acoustic waves in an optical fiber. The sound waves generated on this manner can as an illustration allow a recurrent performance in a telecom optical fiber, which is important to deciphering contextual info resembling language.
Synthetic intelligence is now commonplace and helps us juggle each day duties. Language fashions resembling ChatGPT are in a position to create naturally formulated texts, and summarize paragraphs in a structured manner, thus serving to us to scale back our administrative overheads. The draw back is their monumental vitality necessities, which means that as they evolve, these clever gadgets would require new options to hurry up sign processing and scale back vitality consumption.
Neural networks have the potential to kind the spine of synthetic intelligence. Constructing them as optical neural networks—based mostly on mild as a substitute of electrical indicators—guarantees the dealing with of huge volumes of knowledge at excessive speeds and with nice vitality effectivity. To this point, nonetheless, most of the experimental approaches to implementing optical neural networks have relied on mounted elements and regular gadgets.
Now a global analysis workforce led by Birgit Stiller on the Max-Planck Institute for the Science of Gentle, in collaboration with Dirk Englund from Massachusetts Institute of Know-how, has discovered a method to construct reconfigurable constructing blocks based mostly on sound waves for photonic machine studying. For his or her experimental method, the researchers use hair-thin optical fibers, already globally used for quick web connections.
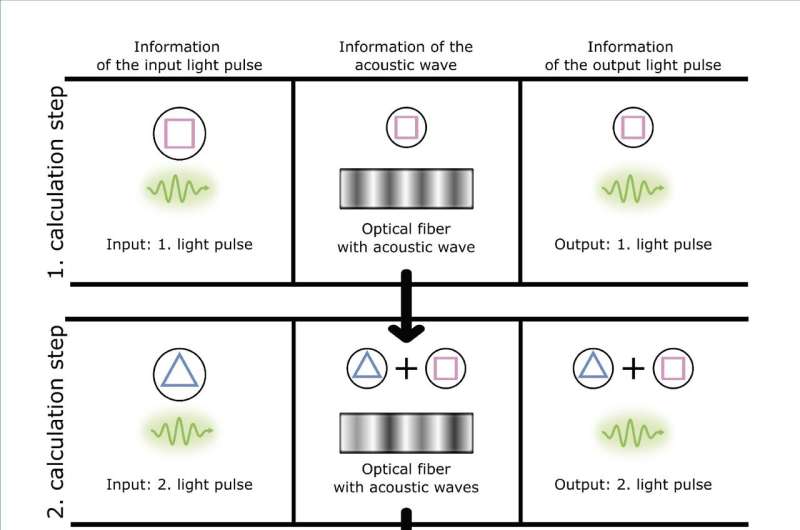
The important thing to the invention is the light-driven creation of touring sound waves that manipulate subsequent computational steps of an optical neural community. Optical info is processed and correlated to acoustic waves. The sound waves have a for much longer transmission time than the optical info stream. Due to this fact, they continue to be within the optical fiber longer and will be linked to every subsequent processing step in flip. The individuality of this course of lies in the truth that it’s utterly managed by mild and doesn’t require sophisticated buildings and transducers.
“I am very excited that we now have launched into this new line of analysis pioneering the usage of sound waves to manage optical neural networks. Our analysis findings have the potential to spark the event of novel constructing blocks for brand new photonic computation architectures,” says Dr. Birgit Stiller, head of the Quantum Optoacoustics Analysis Group.
The primary constructing block experimentally demonstrated by the workforce is a recurrent operator, a know-how extensively used within the area of recurrent neural networks. It permits the linking of a sequence of computational steps and subsequently offers a context for every single calculation step carried out.
In human language, for instance, the order of the phrases can decide the which means of a sentence. For instance, the 2 sentences “She determined to analysis the problem” and “She determined to problem the analysis” include the identical phrases however have completely different meanings. That is due to the completely different contexts created by the orders of the phrases.
A conventional totally linked neural community on a pc faces difficulties capturing context as a result of it requires entry to reminiscence. In an effort to overcome this problem, neural networks have been outfitted with recurrent operations that allow inside reminiscence and are able to capturing contextual info. Though these recurrent neural networks are simple to implement digitally, the analogous implementation in optics is difficult and has up to now relied on synthetic cavities to supply the reminiscence.
The researchers have now used sound waves to implement a recurrent operator. Consequently, the Optoacoustic REcurrent Operator (OREO) harnesses the intrinsic properties of an optical waveguide with out the necessity for a synthetic reservoir or newly fabricated buildings.
OREO provides the benefit of being completely optically managed, making the optoacoustic laptop programmable on a pulse-by-pulse foundation. As an example, the researchers have used this to implement a recurrent dropout optically for the primary time, a regulation method solely beforehand used to spice up the efficiency of digital recurrent neural networks. OREO has been used to differentiate as much as 27 completely different patterns, demonstrating its skill to course of context.
“The all-optical management of OREO is a robust characteristic. Particularly the chance to program the system on a pulse-by-pulse foundation offers a number of further levels of freedom. Utilizing sound waves for photonic machine studying is disrupting the established order and I’m very desperate to see how the sector will evolve sooner or later,” says Steven Becker, doctoral scholar within the Stiller Lab.
Sooner or later, utilizing sound waves for optical neural networks might unlock a brand new class of optical neuromorphic computing which might be reconfigured spontaneously and would enable large-scale in-memory computing within the current telecommunication community. Additionally, on-chip implementations of optical neural networks can profit from this method, which is implementable in photonic waveguides with out further digital controls.
“Photonic machine studying would possibly maintain enormous potential for parallel processing of knowledge and energy-efficient operations. Including acoustic waves can contribute to this endeavor with an all-optically-controlled and easy-to-operate tool-kit,” says Dr. Birgit Stiller.
Extra info:
Steven Becker, Dirk Englund, and Birgit Stiller, An optoacoustic field-programmable perceptron for recurrent neural networks, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-47053-6. www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-47053-6
Quotation:
Utilizing sound waves for photonic machine studying: Examine lays basis for reconfigurable neuromorphic constructing blocks (2024, April 16)
retrieved 28 April 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-04-photonic-machine-lays-foundation-reconfigurable.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




