A primary-ever stretchy digital pores and skin might equip robots and different units with the identical softness and contact sensitivity as human pores and skin, opening up new prospects to carry out duties that require quite a lot of precision and management of power.
The brand new stretchable e-skin, developed by researchers at The College of Texas at Austin, solves a serious bottleneck within the rising know-how. Present e-skin know-how loses sensing accuracy as the fabric stretches, however that’s not the case with this new model.
“Very similar to human pores and skin has to stretch and bend to accommodate our actions, so too does e-skin,” mentioned Nanshu Lu, a professor within the Cockrell Faculty of Engineering’s Division of Aerospace Engineering and Engineering Mechanics who led the challenge. “Regardless of how a lot our e-skin stretches, the strain response would not change, and that could be a important achievement.”
The brand new analysis is published in Matter.
Lu envisions the stretchable e-skin as a vital part to a robotic hand able to the identical degree of softness and sensitivity in contact as a human hand. This may very well be utilized to medical care, the place robots might examine a affected person’s pulse, wipe the physique or therapeutic massage a physique half.
Why is a robotic nurse or bodily therapist needed? All over the world, hundreds of thousands of individuals are getting old and in want of care, greater than the worldwide medical system can present.
“Sooner or later, if now we have extra aged than accessible caregivers, it will be a disaster worldwide,” Lu mentioned. “We have to discover new methods to handle folks effectively and in addition gently, and robots are an vital piece of that puzzle.”
Past medication, human-caring robots may very well be deployed in disasters. They might seek for injured and trapped folks in an earthquake or a collapsed constructing, for instance, and apply on-the-spot care, reminiscent of administering CPR.
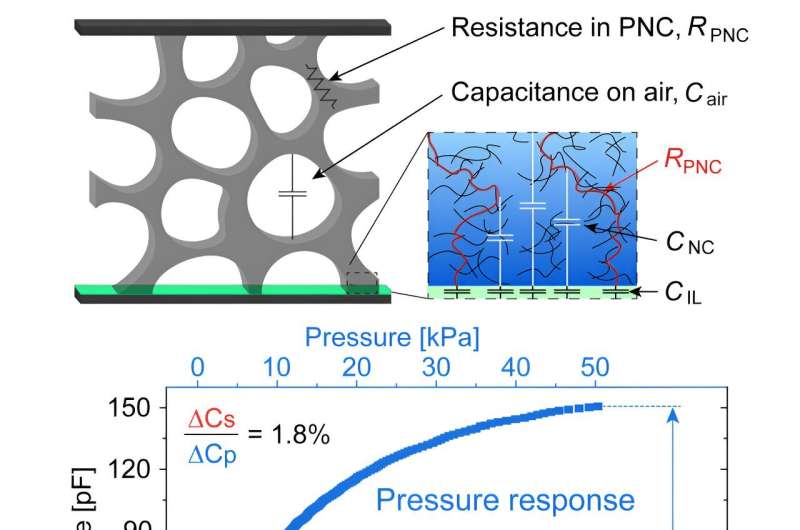
E-skin know-how senses strain from contact, letting the connected machine know the way a lot power to make use of, for instance, to seize a cup or contact an individual. However, when standard e-skin is stretched, it additionally senses that deformation. That studying creates extra noise that skews the sensors’ potential to sense the strain. That would result in a robotic utilizing an excessive amount of power to seize one thing.
In demonstrations, the stretchability allowed the researchers to create inflatable probes and grippers that might change form to carry out quite a lot of delicate, touch-based duties. The inflated skin-wrapped probe was used on human topics to seize their pulse and pulse waves precisely. The deflated grippers can conformably maintain on to a pitcher with out dropping it, even when a coin is dropped inside. The system additionally pressed on a crispy taco shell with out breaking it.
The important thing to this discovery is an modern hybrid response strain sensor that Lu and collaborators have been engaged on for years. Whereas standard e-skins are both capacitive or resistive, the hybrid response e-skin employs each responses to strain. Perfecting these sensors, and mixing them with stretchable insulating and electrode supplies, enabled this e-skin innovation.
Lu—who can be affiliated with the Division of Biomedical Engineering, the Chandra Household Division of Electrical and Pc Engineering, the Walker Division of Mechanical Engineering, and the Texas Supplies Institute—and her group at the moment are working towards the potential functions. They’re collaborating with Roberto Martin-Martin, assistant professor on the Faculty of Pure Sciences’ Pc Science Division to construct a robotic arm outfitted with the e-skin. The researchers and UT have filed a provisional patent utility for the e-skin know-how, and Lu is open to collaborating with robotics firms to carry it to market.
Extra info:
Kyoung-Ho Ha et al, Stretchable hybrid response strain sensors, Matter (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.matt.2024.04.009
Quotation:
Stretchable e-skin might give robots human-level contact sensitivity (2024, Could 2)
retrieved 3 Could 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-05-stretchable-skin-robots-human-sensitivity.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.