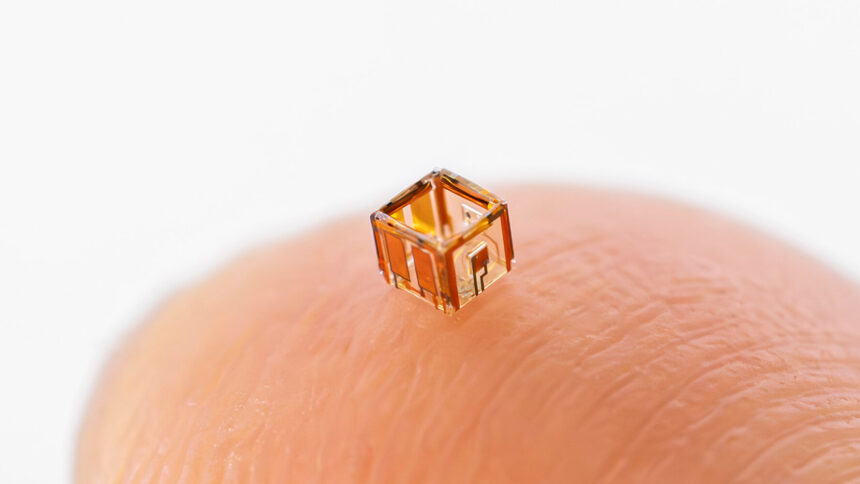
In a significant step towards clever and collaborative microrobotic techniques, researchers on the Analysis Heart for Supplies, Architectures and Integration of Nanomembranes (MAIN) at Chemnitz College of Expertise have developed a brand new technology of autonomous microrobots—termed smartlets—that may talk, reply, and work collectively in aqueous environments.
These tiny units, every only a millimeter in dimension, are totally built-in with onboard electronics, sensors, actuators, and vitality techniques. They can obtain and transmit optical alerts, reply to stimuli with movement, and alternate data with different microrobots of their neighborhood.
The findings are revealed in Science Robotics, in a paper titled “Si chiplet–controlled 3D modular microrobots with smart communication in natural aqueous environments.”
Not like earlier generations of microrobots that relied on a lot bigger wi-fi management setups to mitigate restricted onboard performance, smartlet microrobots are powered by built-in photovoltaic cells, managed by tiny microchips, and able to optical communication by way of embedded micro-LEDs and photodiodes.
“For the primary time, we show a self-contained microrobotic platform that not solely senses and strikes in water but in addition interacts with different microrobots in a completely programmable and autonomous method,” explains Prof. Oliver G. Schmidt, one of many corresponding authors of the examine and Scientific Director of MAIN.
The microrobots are constructed utilizing a versatile origami-inspired strategy, based mostly on sensible multilayer patterned supplies, permitting the flat digital system to roll and fold up autonomously right into a tiny scroll-adorned hole 3D dice, with inside in addition to exterior performance. This opens up the additional floor area wanted for every dice to hold its personal photo voltaic vitality harvester, computational logic, and an optical signaling system, along with interacting exterior faces and inboard locomotion.
When immersed in water, these smartlets can transfer up and down by buoyancy forces created by bubble-generating engines that fill the hole inside of the smartlet with gasoline. They will additionally emit pulses of optical alerts to broadcast directions to different smartlets close by.
This setup permits multi-robotic interactions in water, together with stimulus-driven motion, synchronization, and coordination amongst a number of smartlets. For instance, when one unit receives a light-weight sign, it will possibly decode the knowledge utilizing its onboard processor, triggering a coordinated movement or habits in others.
“The concept of utilizing gentle as each vitality and knowledge opens up a compact and scalable technique to create distributed robotic techniques,” provides Dr. Vineeth Bandari, co-corresponding creator and analysis group chief at MAIN.

One of many key improvements lies within the smartlets’ use of a “wi-fi communication loop” that doesn’t require any exterior cameras, magnets, or antennas.
Optical messages are interpreted domestically on every robotic utilizing custom-coded logic saved on their microchips. The smartlets make use of revolutionary soft-bonding to origami-films to connect {custom} microscopic silicon chiplets, referred to as lablets, which have been developed in an earlier challenge led by Prof. Dr. John McCaskill, a co-corresponding creator and member of MAIN. This allows decentralized management and collaboration—a necessary basis for creating robotic collectives that behave in a coordinated but versatile manner.
Past the laboratory, the potential purposes of such microrobots are wide-ranging. As a result of they’re untethered, biocompatible, and in a position to answer environmental cues, these units may sooner or later help in duties similar to monitoring water high quality, performing minimally invasive medical diagnostics, or probing confined organic environments.
Their capacity to kind interactive, stimulus-responsive colonies may be utilized in smooth robotics, autonomous inspection techniques, or distributed sensing networks.
Dr. Yeji Lee, co-author and specialist in energetic multi-layer microfabrication, whose just lately accomplished Ph.D. analysis supplied very important contributions, emphasizes that this work is only the start. “We’re exploring methods to additional enhance autonomy by including chemical and acoustic sensing modules. These smartlets may evolve into multifunctional platforms that sense, act, and adapt in advanced fluidic environments.”
Wanting ahead, the crew envisions the progressive evolution of those microrobots into dynamic techniques that resemble colonies of digital organisms. Very similar to zooids in colonial animals similar to siphonophores, every smartlet can serve a specialised operate—sensing, speaking, shifting—and collectively kind an emergent robotic organism.
“We’re nonetheless removed from creating synthetic life,” cautions Prof. John McCaskill, who was a founding Director of the European Heart for Residing Expertise in Venice, “however we’re beginning to see how distributed intelligence and modular {hardware} can construct techniques that start to reflect the adaptive, communicative behaviors of residing collectives.”
By constructing such self-contained, communicative microrobots, the Chemnitz crew shouldn’t be solely addressing elementary challenges in microrobotics but in addition laying the groundwork for future techniques that function, evolve, and even perhaps self-organize—inside water droplets, tissue scaffolds, or miniature ecosystems.
Extra data:
Yeji Lee et al, Si chiplet–managed 3D modular microrobots with sensible communication in pure aqueous environments, Science Robotics (2025). DOI: 10.1126/scirobotics.adu6007
Quotation:
Good microrobots be taught to speak and collaborate in water (2025, August 22)
retrieved 23 August 2025
from https://techxplore.com/information/2025-08-smart-microrobots-communicate-collaborate.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.