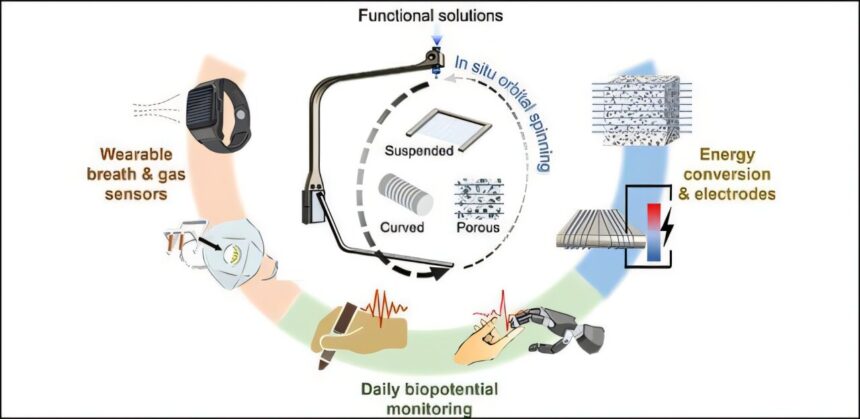
New analysis led by the College of Cambridge, in collaboration with Hong Kong College of Science and Expertise (GZ) and Queen Mary College of London, may redefine how we work together with on a regular basis instruments and units—because of a novel technique for printing ultra-thin conductive microfibers.
Think about fibers thinner than a human hair (nano- to micro-scale in diameter) that may be tuned on-demand so as to add sensing, vitality conversion and digital connectivity capabilities to things of various shapes and floor textures (similar to glass, plastic and leather-based). That is what the researchers have achieved, together with in unconventional supplies like porous graphene aerogels, unlocking new prospects for human-machine interplay in varied on a regular basis settings.
The researchers current a one-step adaptive fiber deposition course of utilizing 3D printing, set as much as fulfill the fast-changing calls for of customers. The method permits the on-demand deployment of conductive materials layers on totally different floor areas, depending on the mannequin’s geometry, on the level of use. The findings are reported within the journal Superior Fiber Supplies.
These clear layers can detect real-time electrocardiogram (ECG) and floor electromyography (sEMG) indicators. The researchers demonstrated this operate utilizing a robotic hand, a pencil and a plier instrument.
Robotic hand
An array of 400 microfibers fabricated from PEDOT:PSS (a conductive polymer), had been printed to wrap across the robotic finger. Throughout ECG measurement, a human index finger was pressed towards the microfibers of the robotic finger.
“This demonstrates a cheap strategy to quickly equip robots with human-interactive sensing features because of PEDOT:PSS microfiber electrodes,” mentioned co-author Stanley Ka, Ph.D. scholar within the Biointerface Analysis Group on the Division of Engineering. “Transient digital skins such because the one demonstrated listed here are essential to allow robots and prosthetics to turn out to be extra human-interactive and mimic the sense of contact.”
The researchers envisage variations of the robotic hand operation, particularly in dwelling care conditions.
In a distant care atmosphere, an interactive robotic is beneficial for home-based care or telemedicine (on this case, performing as a distant monitoring gadget). For the aged, a robotic companion similar to this one may periodically examine important indicators, together with ECG indicators, with out the usage of wearable units. And in sure disaster conditions, the place robotic methods similar to a robotic arm might be deployed, ECG sensing by way of a robotic may assist assess an individual’s cardiac standing earlier than emergency first responders arrive.
Pencil/deal with of a plier instrument
To detect sEMG indicators from the thumb-tendon space when utilizing a pencil or a plier, an array of PEDOT:PSS microfibers (roughly 600 for the pencil and 1,000 for the plier) had been wrapped across the pencil or the plier deal with. The human participant was then requested to jot down with the pencil and lower a inflexible object utilizing the pliers, with totally different ranges of drive.
Combining the above-mentioned on a regular basis duties (writing with a pencil and gripping the deal with of a plier instrument) with real-time biopotential monitoring can alert customers or caregivers to irregular ECG or sEMG patterns. It’s helpful for monitoring people to keep away from overexertion or accidents.
For staff utilizing plier instruments in hazardous environments (e.g., electrical, chemical or excessive warmth), they too might be monitored for indicators of cardiac misery, enabling early intervention in case of fatigue, arrhythmia or different well being dangers. And in high-risk eventualities the place people and robots work collectively to maneuver or manipulate objects, ECG and sEMG information gathered from the human may inform the robotic’s habits, e.g., by slowing down if the human reveals indicators of stress or fatigue.
“These dry microfiber electrodes are long-lasting, and as soon as the sensing activity is full, the fibers might be simply wiped off with out damaging or staining the unique surfaces of those objects,” mentioned co-author Professor Shery Huang, who leads the Biointerface Analysis Group.
“Our strategy for integrating customizable digital features onto varied present objects as proven, will help in establishing a sustainable Fiber-of-Issues (FoT) future—probably revolutionizing medical diagnostics, remedy, and even creating new types of wearable know-how.”
Extra info:
Stanley Gong Sheng Ka et al, Adaptive Printing of Conductive Microfibers for Seamless Practical Enhancement Throughout Numerous Surfaces and Shapes, Superior Fiber Supplies (2025). DOI: 10.1007/s42765-025-00561-6
Quotation:
Good microfibers flip on a regular basis objects into well being care screens and vitality units (2025, October 1)
retrieved 5 October 2025
from https://techxplore.com/information/2025-10-smart-microfibers-everyday-health-energy.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.