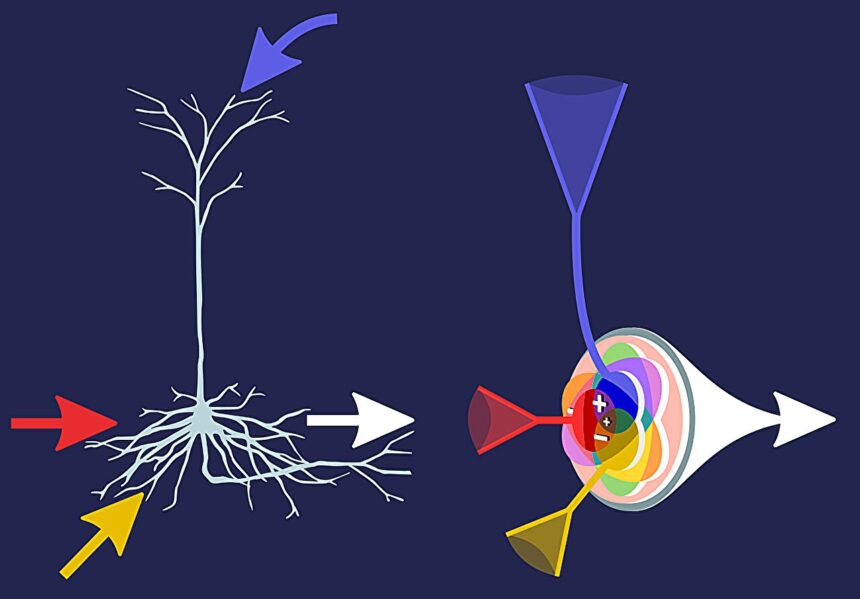
Researchers have developed “infomorphic neurons” that study independently, mimicking their organic counterparts extra precisely than earlier synthetic neurons. A group of researchers from the Göttingen Campus Institute for Dynamics of Organic Networks (CIDBN) on the College of Göttingen and the Max Planck Institute for Dynamics and Self-Group (MPI-DS) has programmed these infomorphic neurons and constructed synthetic neural networks from them.
The particular function is that the person synthetic neurons study in a self-organized manner and draw the mandatory data from their speedy atmosphere within the community. Their findings are published within the journal Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences.
Each the human mind and fashionable synthetic neural networks are extraordinarily highly effective. On the lowest stage, the neurons work collectively as relatively easy computing models.
A synthetic neural community sometimes consists of a number of layers composed of particular person neurons. An enter sign passes by way of these layers and is processed by synthetic neurons as a way to extract related data. Nevertheless, typical synthetic neurons differ considerably from their organic fashions in the way in which they study.
Whereas most synthetic neural networks depend upon overarching coordination outdoors the community as a way to study, organic neurons solely obtain and course of alerts from different neurons of their speedy neighborhood within the community. Organic neural networks are nonetheless far superior to synthetic ones by way of each flexibility and power effectivity.
The brand new synthetic neurons, often called “infomorphic neurons,” are able to studying independently and self-organizing amongst their neighboring neurons. Which means the smallest unit within the community must be managed now not from the surface, however decides itself which enter is related and which isn’t.
In growing the infomorphic neurons, the group was impressed by the way in which the mind works, particularly by the pyramidal cells within the cerebral cortex. These additionally course of stimuli from totally different sources of their speedy atmosphere and use them to adapt and study. The brand new synthetic neurons pursue very common, easy-to-understand studying targets.
“We now instantly perceive what is occurring contained in the community and the way the person synthetic neurons study independently,” emphasizes Marcel Graetz from CIDBN.
By defining the training targets, the researchers enabled the neurons to seek out their particular studying guidelines themselves. The group centered on the training course of of every particular person neuron.
They utilized a novel information-theoretic measure to exactly alter whether or not a neuron ought to search extra redundancy with its neighbors, collaborate synergistically, or attempt to specialise in its personal a part of the community’s data.
“By specializing in sure points of the enter and coordinating with their neighbors, our infomorphic neurons discover ways to contribute to the general job of the community,” explains Valentin Neuhaus from MPI-DS.
With the infomorphic neurons, the group shouldn’t be solely growing a novel methodology for machine studying, however can be contributing to a greater understanding of studying within the mind.
Extra data:
Abdullah Makkeh et al, A common framework for interpretable neural studying primarily based on native information-theoretic objective features, Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences (2025). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2408125122
Quotation:
Self-organizing ‘infomorphic neurons’ can study independently (2025, March 31)
retrieved 1 April 2025
from https://techxplore.com/information/2025-03-infomorphic-neurons-independently.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.