The worldwide transfer towards extra sustainable, inexperienced vitality has elevated energy reserves and the demand for vitality storage units. Sadly, some supplies for these units may be costly and environmentally problematic. Producing different vitality storage units from issues which can be often thrown away might assist resolve these challenges.
Now, researchers in ACS Utilized Supplies & Interfaces report a way to rework rooster fats into carbon-based electrodes for supercapacitors that retailer vitality and energy LEDs.
In 2023, world renewable vitality capability skilled an unprecedented virtually 50 p.c enhance versus the earlier 12 months, in accordance with the Worldwide Power Company. However that extra vitality should be saved someplace for the world to profit from its manufacturing later. For instance, sunny days in California have just lately triggered detrimental vitality costs as a consequence of extra provide from rooftop photo voltaic panels.
Latest efforts to design high-performance storage units have taken benefit of carbon supplies, equivalent to graphene, due to their environment friendly cost transportation and pure abundance, however their fabrication is dear and generates air pollution and greenhouse gases.
On the lookout for another carbon supply materials, Mohan Reddy Pallavolu, Jae Hak Jung, Sang Woo Joo, and colleagues needed to develop a easy, cost-effective technique for changing waste rooster fats into electrically conductive nanostructures for supercapacitor vitality storage units.
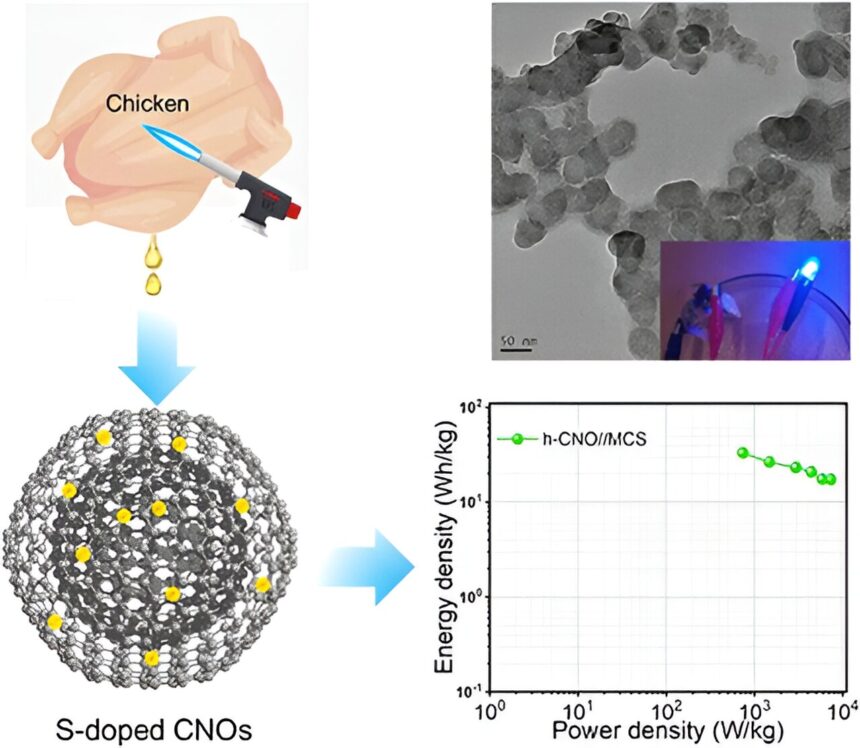
The researchers first used a gasoline flame gun to render the fats from a rooster and burned the melted oil utilizing a flame wick technique, a lot as one would use an oil lamp. They then collected the soot on the underside of a flask, which was suspended above the flame.
Electron microscopy confirmed that the soot contained carbon-based nanostructures that have been uniform spherical lattices of concentric graphite rings, just like the layers of onions. The researchers examined a approach to improve {the electrical} traits of the carbon nanoparticles by soaking them in an answer of thiourea.
Assembled into the detrimental electrode of an uneven supercapacitor, the rooster fat-sourced carbon nanoparticles demonstrated good capacitance and sturdiness, in addition to excessive vitality and energy density. As predicted, these properties have been improved additional when the electrodes have been manufactured from the thiourea-treated carbon nanoparticles.
The researchers then demonstrated that the brand new supercapacitor might carry out real-time functions—charging and connecting two of them to gentle up crimson, inexperienced, and blue LEDs. The outcomes spotlight the potential benefits of utilizing meals waste like rooster fats as a carbon supply within the seek for even greener inexperienced vitality.
Extra data:
Jyothi Nallapureddy et al, Strategic Approach of Synthesizing Heteroatom-Doped Carbon Nano-onions Utilizing Waste Hen Fats Oil for Power Storage Gadgets, ACS Utilized Supplies & Interfaces (2024). DOI: 10.1021/acsami.4c02753
Quotation:
Scientists convert rooster fats into vitality storage units (2024, Might 10)
retrieved 11 Might 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-05-scientists-chicken-fat-energy-storage.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.