In a possible step towards sending small spacecraft to the celebs, researchers have developed an ultra-thin, ultra-reflective membrane designed to experience a column of laser gentle to unbelievable speeds.
Since its launch in 1977, NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft has traveled over 15 billion miles into deep area. That is a good distance—but it surely’s not even 1% of the space to Alpha Centauri, the closest star to the solar. If people are going to ship ships to the celebs, area journey should get rather a lot quicker.
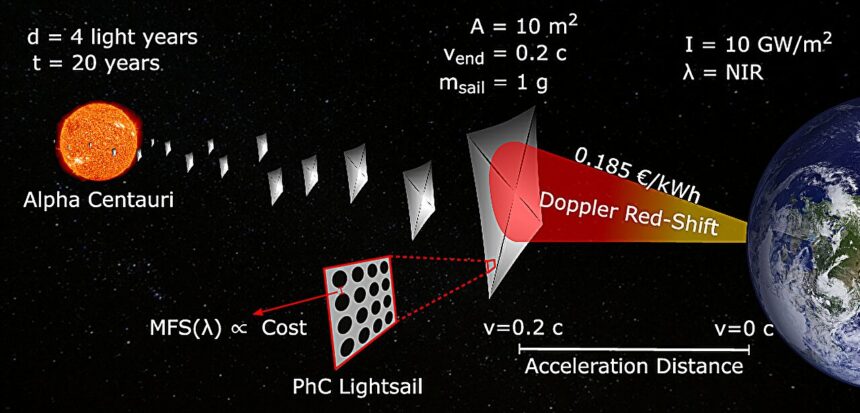
One promising option to decide up that sort of pace is a “lightsail”—a skinny, reflective membrane that may be pushed by gentle a lot the identical manner that wind pushes a sailboat. Lightsails have the potential to cut back flight time to close by stars from a number of thousand years utilizing present propulsion programs to maybe only a decade or two.
Now, a staff of researchers from Brown College and Delft College of Know-how (TU Delft) within the Netherlands has developed a brand new manner of designing and fabricating ultra-thin, ultra-reflective membranes for lightsails.
In a examine published in Nature Communications, the researchers describe a lightsail membrane that is 60 millimeters (about 2.4 inches) vast by 60 millimeters lengthy, however with a thickness of simply 200 nanometers—a tiny fraction of a human hair.
The floor is intricately patterned with billions of nanoscale holes, which assist to cut back the fabric’s weight and enhance its reflectivity, giving it extra acceleration potential.
“This work was a joint effort between theorists at Brown College and experimentalists at TU Delft, making it doable to design, fabricate and check a extremely reflective lightsail with the most important side ratio recorded thus far,” mentioned Miguel Bessa, an affiliate professor in Brown’s College of Engineering who co-led the analysis with Richard Norte, an affiliate professor at TU Delft.
“The experimental breakthrough of Richard’s staff proves their fabrication course of is scalable to the scale wanted for interstellar journey and may be finished in an economical method. Concurrently, my staff may be very enthusiastic to see the important function of our newest optimization methodology guided by machine studying in fixing such an fascinating and troublesome engineering drawback.”
The analysis is a major step towards realizing targets like these of the Starshot Breakthrough Initiative, based by entrepreneur Yuri Milner and the late physicist Stephen Hawking.
The purpose is to make use of ground-based lasers to energy tons of of meter-scale lightsails carrying microchip-sized spacecraft. This new lightsail design might be scaled as much as meter scale pretty simply, the researchers say, and with a manageable price ticket.
For his or her design, the staff used single-layer silicon nitride, a light-weight and high-strength materials that is well-suited for lightsail design. The researchers then labored to maximise its reflectivity whereas minimizing its weight.
The reflectivity of the floor determines how a lot gentle strain is created behind the sail, which in flip determines how briskly it could speed up. On the identical time, a lighter materials requires much less power to speed up, so much less mass equals extra pace.
The optimization course of concerned designing a sample of nanoscale holes—billions of them throughout the fabric’s floor with diameters smaller than the wavelength of sunshine. Bessa’s staff, together with Brown Ph.D. scholar Shunyu Yin, used a brand new synthetic intelligence methodology they developed to optimize the form and placement of the holes for elevated reflectivity and decreased weight.
As soon as that they had an optimized design, a staff led by Norte at TU Delft went to work fabricating it within the lab.
“We now have developed a brand new gas-based etch that enables us to delicately take away the fabric underneath the sails, leaving solely the sail,” Norte mentioned. “If the sails break, it is probably throughout manufacturing. As soon as the sails are suspended, they’re really fairly sturdy. These methods have been uniquely developed at TU Delft.”
Fabricating this design with conventional strategies would have been costly and brought so long as 15 years, the researchers say. However utilizing Norte’s methods, fabrication took a few day and is 1000’s of occasions inexpensive.
The result’s a membrane that the researchers imagine has the very best side ratio—centimeter-scale size however with nanoscale thickness—of any lightsail design thus far. The researchers hope that their strategies is not going to solely assist people attain the celebs, but in addition push the bounds of nanoscale engineering.
“The brand new machine studying and optimization methods we used listed here are very basic,” Bessa mentioned. “We may use them to create a number of various things for various functions. That is actually just the start. We is perhaps on the verge of fixing engineering issues which have remained unsolvable so far.”
Extra data:
Lucas Norder et al, Pentagonal photonic crystal mirrors: scalable lightsails with enhanced acceleration by way of neural topology optimization, Nature Communications (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-57749-y
Quotation:
Researchers develop new design and fabrication methodology to make lightsails for interstellar journey (2025, March 30)
retrieved 30 March 2025
from https://techxplore.com/information/2025-03-fabrication-method-lightsails-interstellar.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.