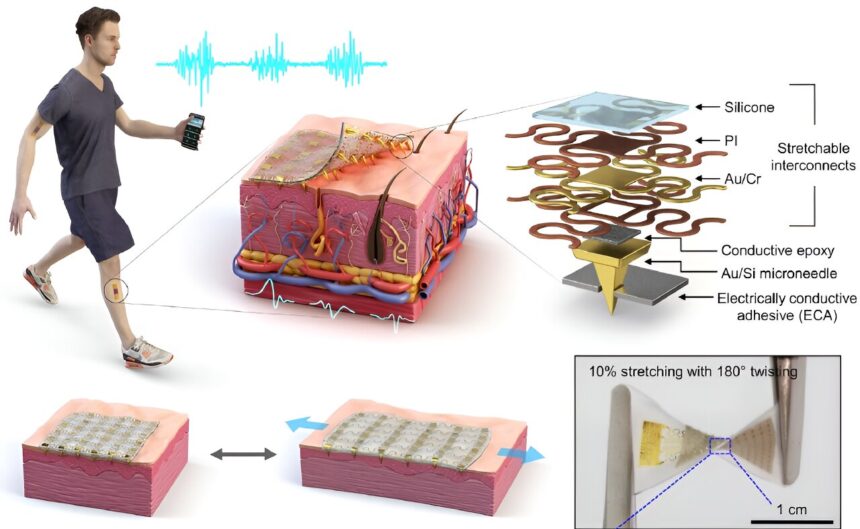
New electromyography (EMG) sensor technology that allows the long-term stable control of wearable robots and is not affected by the wearer’s sweat and dead skin has gained attention recently. Wearable robots are devices used across a variety of rehabilitation treatments for the elderly and patients recovering from stroke or trauma.
A joint research team led by Professor Jae-Woong Jung from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering (EE) and Professor Jung Kim from the KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering (ME) has successfully developed a stretchable and adhesive microneedle sensor that can electrically sense physiological signals at a high level without being affected by the state of the user’s skin.
The results of this research, written by co-first authors Heesoo Kim and Juhyun Lee, who are both Ph.D. candidates in the KAIST School of EE, were published in Science Advances under the title “Skin-preparation-free, stretchable microneedle adhesive patches for reliable electrophysiological sensing and exoskeleton robot control.”
For wearable robots to recognize the intentions behind human movement for their use in rehabilitation treatment, they require a wearable electrophysiological sensor that gives precise EMG measurements. However, existing sensors often show deteriorating signal quality over time and are greatly affected by the user’s skin conditions. Furthermore, the sensor’s higher mechanical hardness causes noise since the contact surface is unable to keep up with the deformation of the skin. These shortcomings limit the reliable, long-term control of wearable robots.
However, the recently developed technology is expected to allow long-term and high-quality EMG measurements as it uses a stretchable and adhesive conducting substrate integrated with microneedle arrays that can easily penetrate the stratum corneum without causing discomfort.
Through its excellent performance, the sensor is anticipated to be able to stably control wearable robots over a long period of time regardless of the wearer’s changing skin conditions and without the need for a preparation step that removes sweat and dead cells from the surface of their skin.
The research team created a stretchable and adhesive microneedle sensor by integrating microneedles into a soft silicon polymer substrate. The hard microneedles penetrate through the stratum corneum, which has high electrical resistance.
The sensor can effectively lower contact resistance with the skin and obtain high-quality electrophysiological signals regardless of contamination. At the same time, the soft and adhesive conducting substrate can adapt to the skin’s surface and stretch with the wearer’s movement, providing a comfortable fit and minimizing noise caused by movement.
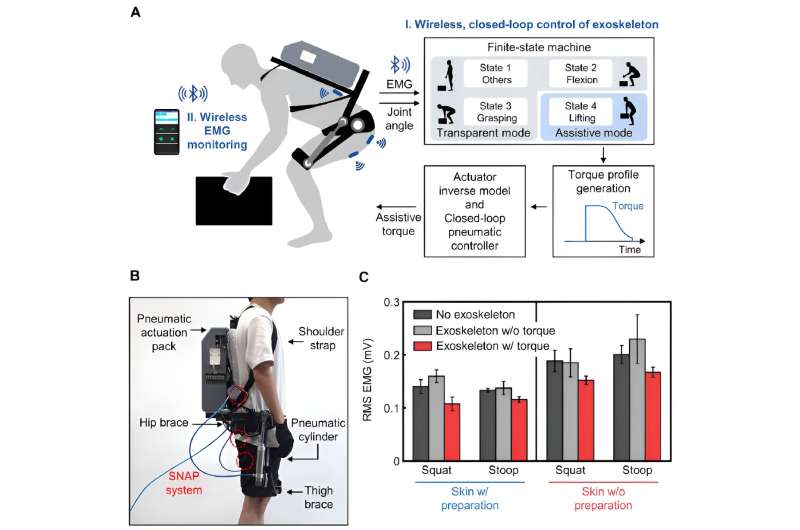
To verify the usability of the new patch, the research team conducted a motion assistance experiment using a wearable robot. They attached the microneedle patch to a user’s leg, where it could sense the electrical signals generated by the muscle. The sensor then sent the detected intention to a wearable robot, allowing the robot to help the wearer lift a heavy object more easily.
Professor Jae-Woong Jung, who led the research, said, “The developed stretchable and adhesive microneedle sensor can stability detect EMG signals without being affected by the state of a user’s skin. Through this, we will be able to control wearable robots with higher precision and stability, which will help the rehabilitation of patients who use robots.”
More information:
Heesoo Kim et al, Skin preparation–free, stretchable microneedle adhesive patches for reliable electrophysiological sensing and exoskeleton robot control, Science Advances (2024). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adk5260
Citation:
Research team develops sweat-resistant wearable robot sensor (2024, January 30)
retrieved 11 February 2024
from https://techxplore.com/news/2024-01-team-resistant-wearable-robot-sensor.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.