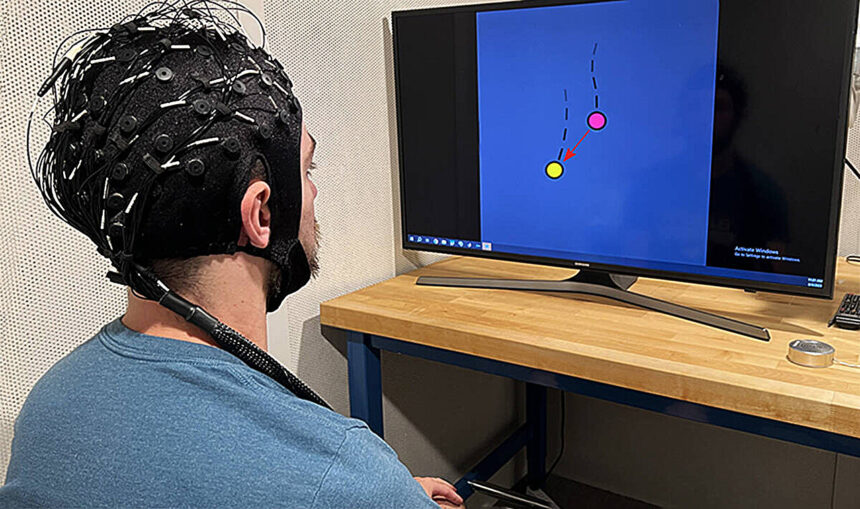
Pursuing a viable various to invasive brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) has been a continued analysis focus of Carnegie Mellon College’s He Lab. In 2019, the group used a noninvasive BCI to efficiently exhibit, for the primary time, {that a} mind-controlled robotic arm had the flexibility to constantly monitor and observe a pc cursor.
As expertise has improved, their AI-powered deep studying strategy has grow to be extra sturdy and efficient. In new work published in PNAS Nexus, the group demonstrates that people can management steady monitoring of a shifting object all by desirous about it, with unmatched efficiency.
Noninvasive BCIs convey a bunch of benefits, in distinction to their invasive counterparts (e.g., Neuralink or Synchron). These embrace elevated security, cost-effectiveness, and a capability for use by quite a few sufferers, in addition to the final inhabitants. Nevertheless, noninvasive BCIs face challenges as a result of their recordings are much less correct and tough to interpret.
In a latest research by Bin He, professor of biomedical engineering at Carnegie Mellon College, a gaggle of 28 human individuals got a posh BCI activity to trace an object in a two-dimensional house all by desirous about it.
Throughout the activity, an electroencephalography (EEG) methodology recorded their exercise, from outdoors the mind. Utilizing AI to coach a deep neural community, the He group then instantly decoded and interpreted human intentions for steady object motion utilizing the BCI sensor information.
Total, the work demonstrates the superb efficiency of noninvasive BCI for a brain-controlled computerized machine.
“The innovation in AI expertise has enabled us to vastly enhance the efficiency versus standard methods, and shed gentle for broad human software sooner or later,” stated Bin He.
Furthermore, the potential of the group’s AI-powered BCI suggests a direct software to constantly controlling a robotic machine.
“We’re at present testing this AI-powered noninvasive BCI expertise to manage refined duties of a robotic arm,” stated He. “Additionally, we’re additional testing its applicability to not solely able-body topics, but additionally stroke sufferers struggling motor impairments.”
In a number of years, this may occasionally result in AI-powered assistive robots turning into obtainable to a broad vary of potential customers.
To this finish, motor-impaired sufferers who’re affected by spinal twine harm, stroke, or different motion impairment, however don’t wish to obtain an implant, stand to learn immensely from analysis on this vein.
“We preserve pushing noninvasive neuroengineering options that may assist everyone,” added He.
Extra data:
Dylan Forenzo et al, Steady monitoring utilizing deep learning-based decoding for noninvasive mind–laptop interface, PNAS Nexus (2024). DOI: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgae145
Quotation:
Refined AI strategy improves noninvasive brain-computer interface efficiency (2024, Might 3)
retrieved 3 Might 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-05-refined-ai-approach-noninvasive-brain.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.