Safety consultants concern Q-Day, the day when quantum computer systems turn out to be so highly effective that they’ll crack immediately’s passwords. Some consultants estimate that at the present time will come throughout the subsequent ten years. Password checks are based mostly on cryptographic one-way features, which calculate an output worth from an enter worth. This makes it doable to examine the validity of a password with out transmitting the password itself: the one-way operate converts the password into an output worth that may then be used to examine its validity in, say, on-line banking.
What makes one-way features particular is that it is unattainable to make use of their output worth to infer the enter worth—in different phrases, the password. At the very least not with immediately’s sources. Nonetheless, future quantum computer systems may make this type of inverse calculation simpler.
Researchers at ETH Zurich have now offered a cryptographic one-way operate that works in a different way from immediately’s and also will be safe sooner or later. Slightly than processing the info utilizing arithmetic operations, it’s saved as a sequence of nucleotides—the chemical constructing blocks of DNA.
Primarily based on true randomness
“Our system relies on true randomness. The enter and output values are bodily linked, and it is solely doable to get from the enter worth to the output worth, not the opposite means spherical,” explains Robert Grass, a professor within the Division of Chemistry and Utilized Biosciences.
“Since it is a bodily system and never a digital one, it could actually’t be decoded by an algorithm, not even by one which runs on a quantum pc,” provides Anne Lüscher, a doctoral pupil in Grass’s group. She is the lead writer of the paper, which was published within the journal Nature Communications.
The researchers’ new system can function a counterfeit-proof means of certifying the authenticity of worthwhile objects akin to artworks. The know-how may be used to hint uncooked supplies and industrial merchandise.
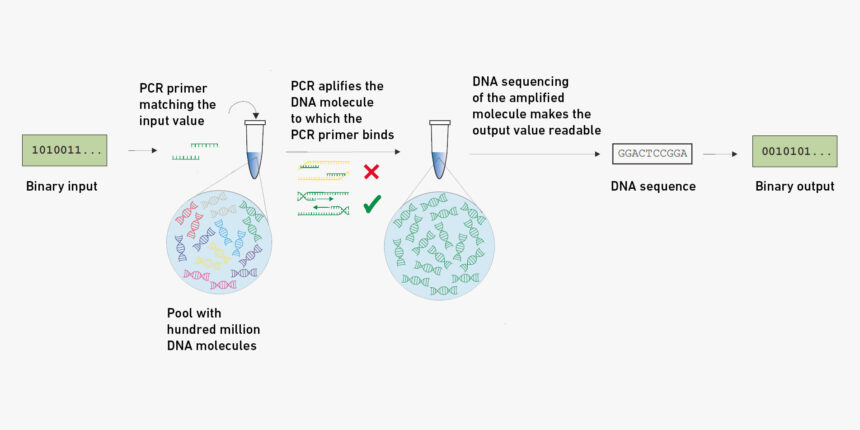
The way it works
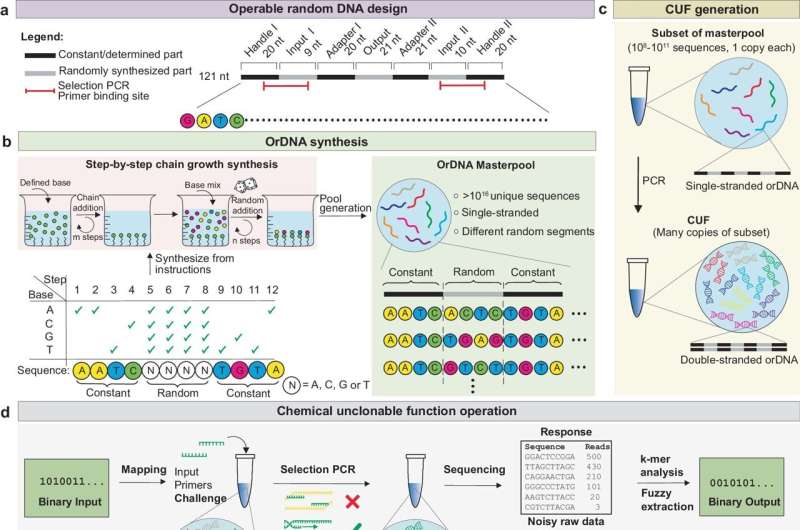
The brand new biochemical one-way operate relies on a pool of 100 million completely different DNA molecules. Every of the molecules comprises two segments that includes a random sequence of nucleotides: one section for the enter worth and one for the output worth. There are a number of hundred an identical copies of every of those DNA molecules within the pool, and the pool can be divided into a number of swimming pools; these are an identical as a result of they include the identical random DNA molecules. The swimming pools may be positioned somewhere else, or they are often constructed into objects.
Anybody in possession of this DNA pool holds the safety system’s lock. The polymerase chain response (PCR) can be utilized to check a key, or enter worth, which takes the type of a brief sequence of nucleotides. In the course of the PCR, this key searches the pool of lots of of hundreds of thousands of DNA molecules for the molecule with the matching enter worth, and the PCR then amplifies the output worth positioned on the identical molecule. DNA sequencing is used to make the output worth readable.
At first look, the precept appears difficult. “Nonetheless, producing DNA molecules with built-in randomness is affordable and simple,” Grass says. The manufacturing prices for a DNA pool that may be divided up on this means are lower than 1 Swiss franc. Utilizing DNA sequencing to learn out the output worth is extra time-consuming and costly, however many biology laboratories already possess the required gear.
Securing worthwhile items and provide chains
ETH Zurich has utilized for a patent on this new know-how. The researchers now wish to optimize and refine it to carry it to market. As a result of utilizing the strategy calls for specialised laboratory infrastructure, the scientists assume the almost definitely software for this type of password verification is at present for extremely delicate items or for entry to buildings with restricted entry. This know-how will not be an choice for the broader public to examine passwords till DNA sequencing specifically turns into simpler.
Somewhat extra thought has already gone into the thought of utilizing the know-how for the forgery-proof certification of artworks. As an illustration, if there are ten copies of an image, the artist can mark all of them with the DNA pool—maybe by mixing the DNA into the paint, spraying it onto the image or making use of it to a selected spot.
If a number of house owners later want to have the authenticity of those artworks confirmed, they’ll get collectively, agree on a key (i.e. an enter worth) and perform the DNA check. All of the copies for which the check produces the identical output worth may have been confirmed real. The brand new know-how may be used to hyperlink crypto-assets akin to NFTs, which exist solely within the digital world, to an object and thus to the bodily world.
Moreover, it might assist counterfeit-proof monitoring alongside provide chains of commercial items or uncooked supplies. “The aviation business, for instance, has to have the ability to present full proof that it makes use of solely unique parts. Our know-how can assure traceability,” Grass says. As well as, the strategy may very well be used to label the authenticity of unique medicines or cosmetics.
Extra data:
Anne M. Luescher et al, Chemical unclonable features based mostly on operable random DNA swimming pools, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-47187-7
Quotation:
Defending artwork and passwords with biochemistry (2024, April 8)
retrieved 9 April 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-04-art-passwords-biochemistry.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.