Mars presents a extremely complicated pure atmosphere, characterised by quite a lot of gasoline elements—95.32% carbon dioxide, 2.7% nitrogen, 1.6% argon, 0.13% oxygen, and 0.08% carbon monoxide—in addition to excessive temperature fluctuations, with day-to-night temperature variations of about 60 °C.
To deal with these challenges, Prof. Peng Tan and Dr. Xu Xiao have developed a novel Mars battery that uniquely makes use of the Martian environment as gas throughout discharge. This method considerably reduces the battery’s weight, making it extra appropriate for house missions.
Their research, “A high-energy-density and long-cycling-lifespan Mars battery,” is published within the journal Science Bulletin.
As soon as depleted, the battery might be recharged utilizing photo voltaic vitality harvested from the Martian floor, enabling it to be ready for subsequent discharges. Moreover, the staff simulated Martian floor situations, together with temperature fluctuations, to develop a Mars battery system able to steady energy output.
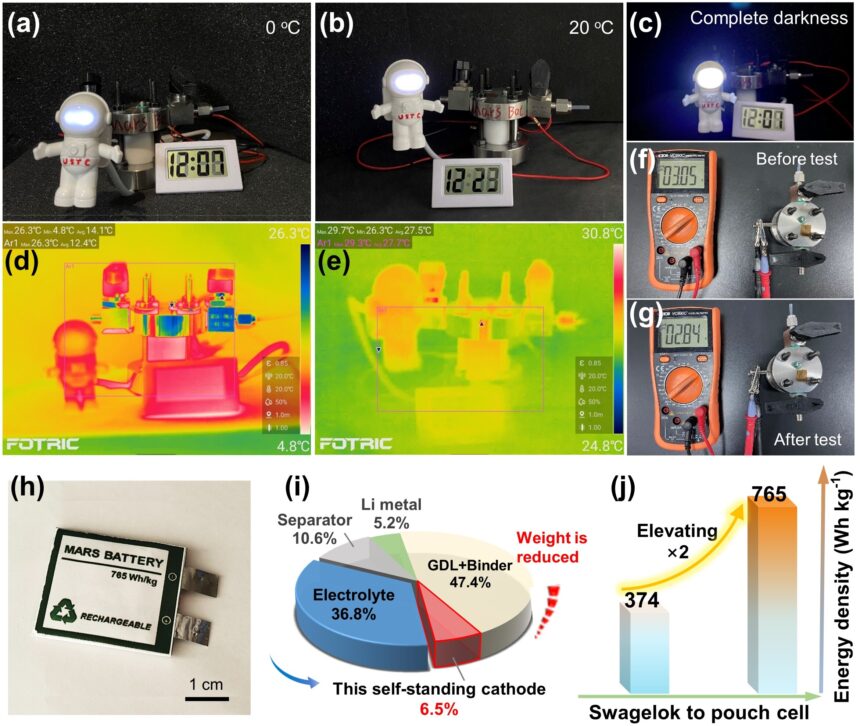
The researchers additionally exhibit that at a low temperature of 0 °C, the battery achieves an vitality density of as much as 373.9 Wh kg-1 and a cost/discharge cycle lifetime of 1,375 hours, which corresponds to roughly two Martian months of steady operation.
The battery’s cost and discharge processes contain the formation and decomposition of lithium carbonate, whereas hint quantities of oxygen and carbon monoxide within the Martian environment act as response catalysts, considerably accelerating the carbon dioxide conversion kinetics.
The staff maximized the efficient response space of the Martian environment via built-in electrode preparation and a folded cell construction design. By enlarging the cell measurement to 4 cm2, they additional enhanced the vitality density of the pouch battery to 765 Wh kg-1 and 630 Wh l-1.
In response to the researchers, this research provides a important proof-of-concept for the applying of Mars batteries in actual Martian environments.
They intention to advance the event of solid-state Mars batteries in future analysis, addressing the challenges of electrolyte volatilization underneath low stress, and supporting thermal and barometric administration methods. This work lays a foundational step towards the event of multi-energy complementary methods for future house exploration.
Extra info:
Xu Xiao et al, A high-energy-density and long-cycling-lifespan Mars battery, Science Bulletin (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.scib.2024.06.033
Quotation:
Proof-of-concept research develops battery that may use Martian environment as gas throughout discharge (2024, September 30)
retrieved 4 October 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-09-proof-concept-battery-martian-atmosphere.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.