As a result of intense international impression of fossil gas overuse on air high quality and local weather, the seek for superior clear vitality options has develop into crucial. Metallic–air batteries provide a game-changing various, holding the potential to exchange combustion engines in numerous purposes.
By electrochemically changing oxygen from the air into energy, these batteries obtain theoretical vitality densities as much as twelve instances larger than lithium-ion cells, delivering unprecedented effectivity with zero operational emissions.
Challenges dealing with metallic–air battery adoption
Regardless of their theoretical benefits, metallic–air batteries have but to attain widespread industrial viability because of a number of crucial obstacles. Present high-performance catalysts primarily rely upon costly valuable metals, equivalent to platinum and ruthenium, rendering them economically unfeasible for mass manufacturing and large-scale deployment.
Moreover, most present catalyst supplies are monofunctional, effectively driving solely one of many two important electrochemical processes—the oxygen discount response (ORR) or the oxygen evolution response (OER)—however not each.
Compounding these points, the complicated, multi-step synthesis processes required for these catalysts inflate manufacturing prices and severely prohibit scalability.
Revolutionary analysis tackles catalyst limitations
Towards this backdrop, a analysis workforce led by Professor Takahiro Ishizaki from the Faculty of Engineering at Shibaura Institute of Know-how, Japan, and Assistant Professor Sangwoo Chae from Nagoya College, Japan, has been working laborious to seek out acceptable options to those points.
Of their newest research, printed in Sustainable Energy & Fuels, they report a revolutionary single-step methodology for creating extremely efficient bifunctional catalysts utilizing plentiful, low-cost supplies.
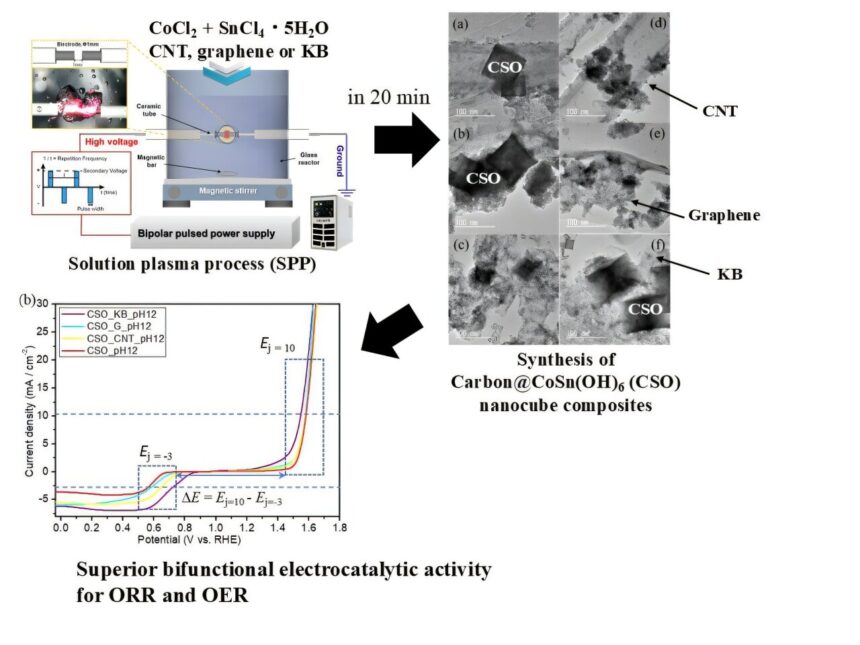
The researchers utilized the lately pioneered resolution plasma course of (SPP) for the synthesis, efficiently creating cobalt-tin hydroxide (CoSn(OH)6) composites anchored to varied carbon helps. This can be a crucial distinction from standard catalyst synthesis: in contrast to conventional, multi-step strategies that require surfactants and in depth post-processing, SPP permits fast, single-step synthesis at room temperature underneath ambient atmospheric circumstances.
This plasma-based method not solely confers distinctive floor properties that considerably increase catalytic exercise but additionally dramatically slashes manufacturing complexity and manufacturing prices.
The analysis workforce systematically produced catalysts with various compositions and carbon buildings, rigorously testing their bifunctional efficiency in each the oxygen discount (ORR) and oxygen evolution (OER) reactions—the 2 pivotal processes figuring out general battery effectivity.
Their best-performing catalyst, combining CoSn(OH)6 with Ketjen Black carbon, achieved outstanding outcomes. For oxygen evolution, it outperformed the industry-standard ruthenium oxide catalyst, requiring decrease voltages to attain the identical present densities. In oxygen discount, it exhibited efficiency corresponding to way more costly platinum-based catalysts whereas relying solely on plentiful supplies.
Furthermore, this new catalyst proved to be fairly sturdy, as Prof. Ishizaki says, “Our superior CoSn(OH)6–Ketjen Black composite exhibited distinctive long-term stability, sustaining its superior oxygen evolution efficiency for over 12 hours with out degradation, a vital issue for real-world battery purposes.”
Notably, the catalyst’s potential to effectively catalyze each required reactions represents a big development within the discipline. The researchers measured a possible hole of simply 0.835 V between the 2 reactions, thus enabling extremely environment friendly vitality conversion. This twin performance eliminates the necessity for separate catalysts, additional lowering system complexity and prices.
Detailed evaluation confirms that the superior catalytic efficiency stems from highly effective synergistic interactions between the (CoSn(OH)6) nanoparticles and the carbon assist.
The researchers found that the SPP synthesis course of is essential: it ensures a uniform distribution of lively nanoparticles throughout the carbon floor, which maximizes the publicity of catalytic websites whereas concurrently guaranteeing glorious electrical conductivity.
Moreover, the strategy affords exact management over particle dimension and essential floor properties, permitting for systematic optimization of catalytic exercise.
“This breakthrough holds profound potential to customise and manufacture high-performance, sturdy, and low-cost bifunctional electrocatalysts for crucial vitality conversion programs,” highlights Prof. Ishizaki. “It affords a very sustainable materials various to commercially used valuable metal-based catalysts.”
Implications for vitality storage and {industry}
The implications of this work are far-reaching, promising a revolution throughout the vitality sector. Metallic–air batteries powered by these newly developed catalysts might basically remodel vitality storage for electrical autos, providing a considerably longer vary and quicker charging capabilities whereas concurrently lowering general prices.
Moreover, the expertise holds immense potential for grid-scale vitality storage, which is essential for the environment friendly integration of intermittent renewable sources like photo voltaic and wind energy into electrical networks. The proposed single-step synthesis methodology affords equally profound industrial benefits.
By eliminating complicated, multi-step processing and reliance on costly uncooked supplies, producers can produce these high-performing catalysts at a fraction of the present value. Furthermore, the flexibility to synthesize these supplies underneath ambient circumstances drastically reduces vitality consumption and environmental impression in comparison with standard high-temperature, high-pressure strategies presently utilized in battery and catalyst manufacturing.
Total, this analysis represents a vital and transformative step towards attaining economically viable clear vitality storage on a worldwide scale, poised to considerably speed up the important transition away from fossil fuels within the transportation and vitality sectors.
Extra info:
Sangwoo Chae et al, Single-step resolution plasma synthesis of bifunctional CoSn(OH)6–carbon composite electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution and oxygen discount reactions, Sustainable Vitality & Fuels (2025). DOI: 10.1039/d5se00370a
Quotation:
Plasma-based methodology creates environment friendly, low-cost catalysts for metallic–air batteries (2025, November 17)
retrieved 17 November 2025
from https://techxplore.com/information/2025-11-plasma-based-method-efficient-catalysts.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.