College of Oxford researchers have made a big step in direction of realizing miniature, mushy batteries to be used in quite a lot of biomedical purposes, together with the defibrillation and pacing of coronary heart tissues. The work has been revealed within the journal Nature Chemical Engineering.
The event of tiny sensible gadgets, smaller than just a few cubic millimeters, calls for equally small energy sources. For minimally invasive biomedical gadgets that work together with organic tissues, these energy sources have to be fabricated from mushy supplies.
Ideally, these also needs to have options reminiscent of excessive capability, biocompatibility and biodegradability, triggerable activation, and the power to be managed remotely. So far, there was no battery that may fulfill these necessities unexpectedly.
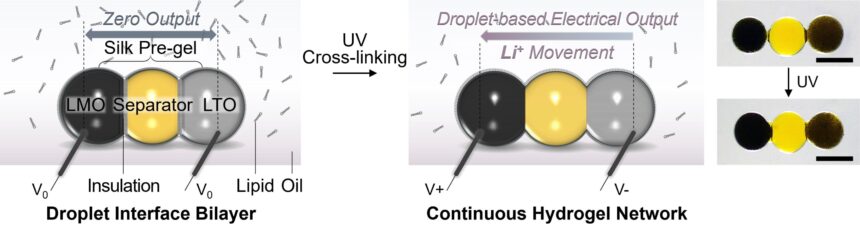
To handle these necessities, researchers from the College of Oxford’s Division of Chemistry and Division of Pharmacology have developed a miniature, mushy lithium-ion battery constructed from biocompatible hydrogel droplets.
Surfactant-supported meeting (meeting aided by soap-like molecules), a technique reported by the same group final yr within the journal Nature, is used to attach three microscale droplets of 10 nanoliters of quantity. Totally different lithium-ion particles contained in every of the 2 ends then generate the output vitality.

“Our droplet battery is light-activated, rechargeable, and biodegradable after use. So far, it’s the smallest hydrogel lithium-ion battery and has a superior vitality density,” mentioned Dr. Yujia Zhang (Division of Chemistry, College of Oxford), the lead researcher for the research and a beginning Assistant Professor on the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne.
“We used the droplet battery to energy the motion of charged molecules between artificial cells and to regulate the beating and defibrillation of mouse hearts. By together with magnetic particles to regulate motion, the battery may also perform as a cell vitality provider.”
Proof-of-concept coronary heart therapies had been carried out within the laboratory of Professor Ming Lei (Division of Pharmacology), a senior electrophysiologist in cardiac arrhythmias. He mentioned, “Cardiac arrhythmia is a number one reason for demise worldwide. Our proof-of-concept software in animal fashions demonstrates an thrilling new avenue of wi-fi and biodegradable gadgets for the administration of arrhythmias.”
Professor Hagan Bayley (Division of Chemistry), the analysis group chief for the research, mentioned, “The tiny mushy lithium-ion battery is essentially the most refined in a sequence of microscale energy packs developed by Dr. Zhang and factors to a improbable future for biocompatible digital gadgets that may function below physiological situations.”
The researchers have filed a patent software by Oxford College Innovation. They envisage that the tiny versatile battery, notably related to small-scale robots for bioapplications, will open up new potentialities in varied areas together with medical medication.
Extra data:
A microscale mushy lithium-ion battery for tissue stimulation, Nature Chemical Engineering (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s44286-024-00136-z
Quotation:
Miniature mushy lithium-ion battery provides new potentialities for bio-integrated gadgets and robotics (2024, October 25)
retrieved 25 October 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-10-miniature-soft-lithium-ion-battery.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.