The 6G4Society mission goals to combine societal, environmental, and financial values into the event of 6G expertise, making certain that developments in connectivity align with moral requirements and sustainability rules.
Debates on sustainability, digital rights, and accountable innovation present that being technically viable is now not sufficient. What issues is not only whether or not applied sciences are adopted but additionally their acceptability and trustworthiness, their alignment with moral expectations, their contribution to sustainability, and their reflection of shared social values. As the event of 6G expertise progresses, these questions are central to its legitimacy. The 6G4Society mission explores how 6G can combine societal, environmental, and financial dimensions into innovation itself.
Europe’s 6G imaginative and prescient hyperlinks expertise with sustainability, policy, and ethics. The Sensible Networks and Companies Joint Endeavor (SNS JU) offers the analysis and innovation framework, supporting initiatives reminiscent of 6G4Society, which explores how 6G expertise can align with European values of inclusivity, belief, and sustainability.
This broad coverage panorama displays a rising European consensus: 6G have to be not solely sooner or extra environment friendly, but additionally a catalyst for environmental, social, and financial sustainability.¹ The 6G4Society mission, alongside different SNS initiatives, drives the shift by creating sustainability-oriented enterprise fashions and measurable indicators linking technological progress to real-world advantages and to sustainability. These fashions embody ideas reminiscent of Sustainability-as-a-Platform, round useful resource marketplaces, and impact-driven partnerships, all designed to maneuver from volume-based metrics towards value-based outcomes.¹
Sustainability on the coronary heart of European connectivity
6G4Society was created to make sure that societal and environmental values aren’t afterthoughts however the basis of technological progress. By means of collaboration between social scientists, engineers, residents, and policymakers, the mission seeks to develop sensible instruments and frameworks that make social acceptability and sustainability measurable, actionable, and indispensable to Europe’s digital future.
Europe should depend on extra holistic levers: frameworks, public engagement, value-based indicators, cross-project synergies, and coverage integration. Beneath, we develop on every of these levers.
Frameworks, not simply specs
The Acceptance Fashions of 6G Expertise framework,² developed by 6G4Society, introduces a structured strategy to assess how new applied sciences resonate with moral norms, cultural contexts, and public belief. As a substitute of focusing solely on KPIs reminiscent of throughput or power effectivity, this framework brings in qualitative and quantitative dimensions – citizen attitudes, inclusivity, and perceived equity.
Embedding such frameworks in analysis initiatives permits societal impacts to be assessed alongside technical outcomes. This displays a broader shift inside the SNS JU: from designing networks for efficiency to designing networks for folks.
Early public engagement
6G4Society locations public engagement on the centre of its mission by actions such because the Citizen Survey, which gathers views from throughout Europe on expectations, fears, and hopes surrounding the following era of networks.
The mission explores participatory mechanisms reminiscent of workshops, focus teams, and living-lab pilots. These are integral elements of policymaking and innovation governance.³ Participating residents early allows builders and policymakers to detect rising considerations earlier than they escalate into resistance.
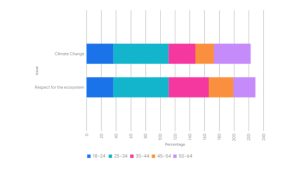
The Citizen Survey, performed in 9 languages and gathering over 1,800 responses, mixed quantitative and qualitative questions designed to keep away from bias and encourage reflection on lived expertise.
The findings spotlight a spectrum of public attitudes, from curiosity and optimism to scepticism and fatigue. Many respondents recognised the potential of 6G to boost every day life by improved entry to info and connectivity with family members. Nevertheless, these expectations had been accompanied by considerations that the fast tempo of technological change may outstrip societal wants.
Throughout age teams, environmental accountability emerged as a unifying precedence. Youthful individuals had been notably conscious of each societal and environmental implications, usually linking connectivity to points reminiscent of power use and materials consumption. Respect for the ecosystem and biodiversity ranked among the many high priorities throughout generations, adopted by local weather change. Members additionally emphasised honest and inclusive entry to connectivity, associating digital fairness with broader concepts of solidarity and social cohesion.
These insights affirm that residents anticipate 6G expertise to be designed with function, transparency, and accountability. The outcomes present an vital reference level for the Social Acceptance Mannequin that 6G4Society is creating, making certain that the following era of connectivity is guided by public values and designed for human and planetary wellbeing.
Key worth and sustainability indicators
A sustainable 6G ecosystem requires new metrics. Conventional KPIs inform us how networks carry out, however not whether or not they advance sustainability or fairness.⁴ To shut this hole, 6G4Society promotes the idea of Key Worth Indicators (KVIs) and Key Sustainability Indicators (KSIs).
These indicators measure dimensions reminiscent of power use and emissions, materials circularity, resilience, equity, inclusiveness, and belief.
Growing KVIs and KSIs additionally allows comparability throughout initiatives and coverage domains, serving to the EU consider whether or not public funding really delivers on its Inexperienced Deal and Digital Decade aims. Inside the SNS JU ecosystem, 6G4Society collaborates with different initiatives to harmonise definitions and methodologies, making certain that sustainability metrics are interoperable and credible.⁵
Cross-project synergies
6G4Society works to create synergies throughout the varied panorama of European analysis and innovation. Collaboration with different SNS JU initiatives ensures that social acceptability and sustainability are mainstreamed reasonably than remoted matters.⁴
This co-operation extends past the SNS JU neighborhood.³ 6G4Society liaises with European and worldwide initiatives on standardisation, regulation, and digital inclusion to align aims and share classes realized. By means of workshops and joint publications, it contributes to constructing a frequent language between engineers, policymakers, and social scientists.⁶
Coverage integration
Lasting affect requires that insights from analysis circulation into coverage and regulation. 6G4Society contributes by mapping how societal values intersect with current and rising legislative frameworks. By analysing these intersections, the mission identifies the place coverage levers can reinforce sustainability and acceptance.⁷
The aim is evident: to make sure that incentives and regulatory mechanisms reward constructive affect. Coverage integration means aligning analysis outcomes with the European Inexperienced Deal, the Digital Decade targets, and the moral rules embedded in EU regulation. It additionally means making certain that sustainability and fairness develop into non-negotiable situations for funding, deployment, and standardisation.
By means of place papers, workshops, and direct dialogue with policymakers, 6G4Society interprets educational perception into actionable steering.⁸
Conclusion: Towards a value-driven 6G future
6G4Society’s work illustrates how Europe can transfer from ambition to implementation in embedding societal and environmental values into technological methods. A 6G community constructed on sustainability and fairness is greater than a technical achievement; it’s a democratic and cultural one. It indicators that Europe’s technological future will likely be measured by the depth of belief, inclusion, and shared profit it delivers.
References
- Calisti, M., Aseeva, A., & Onwude, D. (2025). 6G Sustainability: Prospective Business Models. ACM. https://doi.org/10.1145/3748699.3749820
- 6G4Society mission: D1.1- SOCIETAL ASPECTS IN 6G TECHNOLOGY: CONCERNS, ACCEPTANCE MODELS AND SUSTAINABILITY INDICATORS
- D2.1 PUBLIC ENGAGEMENT STRATEGY AND PLAN
- Rezaki, A., Trichias, Okay., Mesodiakaki, A., Gavras, A., Aseeva, A., Berardinelli, G., Osman, H., Gutiérrez Terán, J., Petersen, Okay., Gramaglia, M., Katz, M., Bezzi, M., & Ghoraishi, M. (Eds.). (2025). Sustainability in SNS JU Tasks – Targets, Methodologies, Commerce-offs and Implementation Issues In the direction of 6G Programs.
- Petersen, K., Bezzi, M., Gavras, A., Calisti, M., & Mohnani, P. (2025). Value Approach of 6G: The Role of Key Value Indicators in Design and Societal Impact.
- 6G4Society mission: D3.1 – Report on Liaison Activities
- 6G4Society mission: D1.2 – In the direction of a socially accepted and sustainably 6G-Coverage Transient
- 6G4Society mission: D4.1 – Dissemination and Communication Strategy and Plan
Please word, this text may also seem within the twenty fourth version of our quarterly publication.




