Three-dimensional (3D) integration has opened new prospects for the event of denser circuits with extra interconnected digital elements. 3D integration approaches entail stacking a number of layers of digital circuits collectively, finally producing extra compact and environment friendly units.
These electronics fabrication methods can scale back each the scale and the facility consumption of electronics whereas additionally boosting their efficiency. An rising 3D integration method that has been discovered to be significantly promising is monolithic 3D (M3D) integration, which entails the development of transistors layer by layer on the identical substrate as an alternative of bonding particular person chips collectively.
Researchers at Pennsylvania State College just lately developed extremely compact near-sensor computing chips through the heterogeneous M3D integration of two-dimensional (2D) supplies. Their paper, published in Nature Electronics, demonstrates the fabrication of those chips utilizing scalable methods which are suitable with present manufacturing processes.
“M3D integration is being more and more adopted by the semiconductor business as an alternative choice to conventional through-silicon through expertise, as a approach to improve the density of stacked, heterogenous digital elements,” Subir Ghosh, Yikai Zheng and their colleagues wrote of their paper. “M3D integration can even present transistor-level partitioning and materials heterogeneity. Nevertheless, there are few large-area demonstrations of M3D integration utilizing non-silicon supplies.”
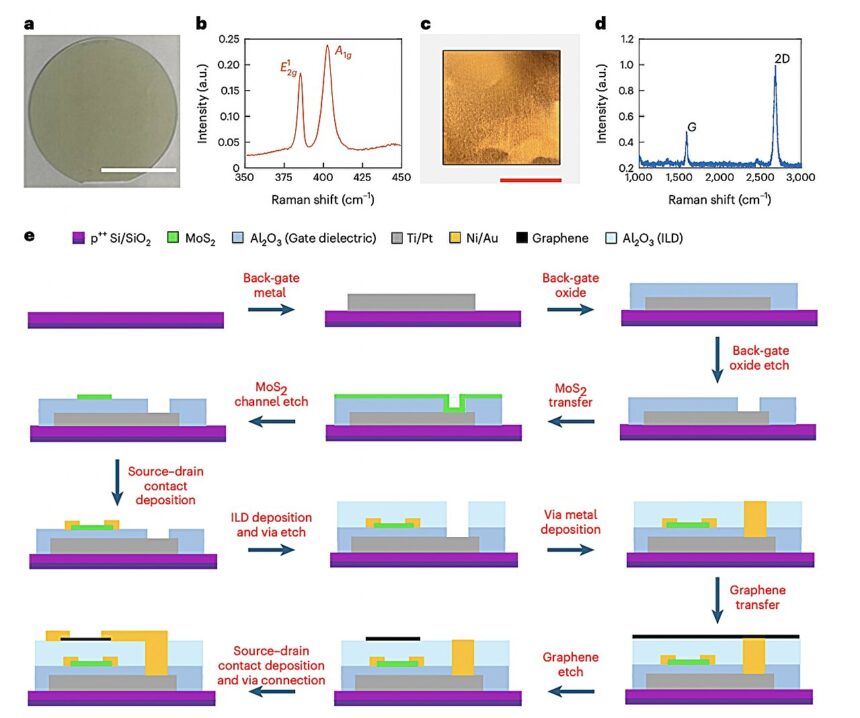
As a part of their latest research, Ghosh, Zheng and their colleagues got down to develop a sensing and near-sensor computing chip based mostly on 2D electronics using an M3D integration technique. The chip they created integrates over 500 chemitransistors and over 500 memtransistors, with vertical interconnects (vias) which are 3 μm in dimension and at a 1 μm distance from one another.
“We report heterogeneous M3D integration of two-dimensional supplies utilizing a dense inter-via construction with an interconnect (I/O) density of 62,500 I/O per mm2,” Ghosh, Zheng and their colleagues wrote. “Our M3D stack consists of graphene-based chemisensors in tier 2 and molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) memtransistor-based programmable circuits in tier 1, with greater than 500 units in every tier. Our course of permits the bodily proximity between sensors and computing components to be decreased to 50 nm, offering decreased latency in near-sensor computing purposes.”
A key benefit of the M3D integration method employed by the researchers is that your complete fabrication course of takes place at temperatures underneath 200 °C. This implies it’s suitable with back-end-of-line integration processes presently used to manufacture semiconductor-based units.
As a part of their research, Ghosh, Zheng and their colleagues used the computing chip they developed for chemical codification. Particularly, they developed an alert system that might be used to determine and classify totally different chemical substances.
The chemitransistors within the workforce’s chip had been uncovered to sugar options with totally different concentrations and {the electrical} indicators they generated in response to those options had been recorded. Subsequently, memtransistors processed the indicators generated by the chemitransistors, changing them into analog and digital codes.
The findings of the workforce’s alert system demonstrations spotlight the potential of the brand new near-sensing computing chip for processing and classifying chemical substances. Sooner or later, their proposed fabrication method might be scaled as much as develop chips with a fair better variety of circuits and sensors, which might sort out extra superior classification duties.
Extra data:
Subir Ghosh et al, Monolithic and heterogeneous three-dimensional integration of two-dimensional supplies with high-density vias, Nature Electronics (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41928-024-01251-8
© 2024 Science X Community
Quotation:
Creating compact near-sensor computing chips through 3D integration of 2D supplies (2024, November 10)
retrieved 10 November 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-11-compact-sensor-chips-3d-Second.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.