A standard digital digital camera splits a picture into three channels—pink, inexperienced and blue—mirroring how the human eye perceives colour. However these are simply three discrete factors alongside a steady spectrum of wavelengths. Specialised “spectral” cameras go additional by sequentially capturing dozens, and even a whole bunch, of those divisions throughout the spectrum.
This course of is sluggish, nevertheless, which means that hyperspectral cameras can solely take nonetheless pictures, or movies with very low body charges, or frames per second (fps). However what if a high-fps video digital camera might seize dozens of wavelengths directly, revealing particulars invisible to the bare eye?
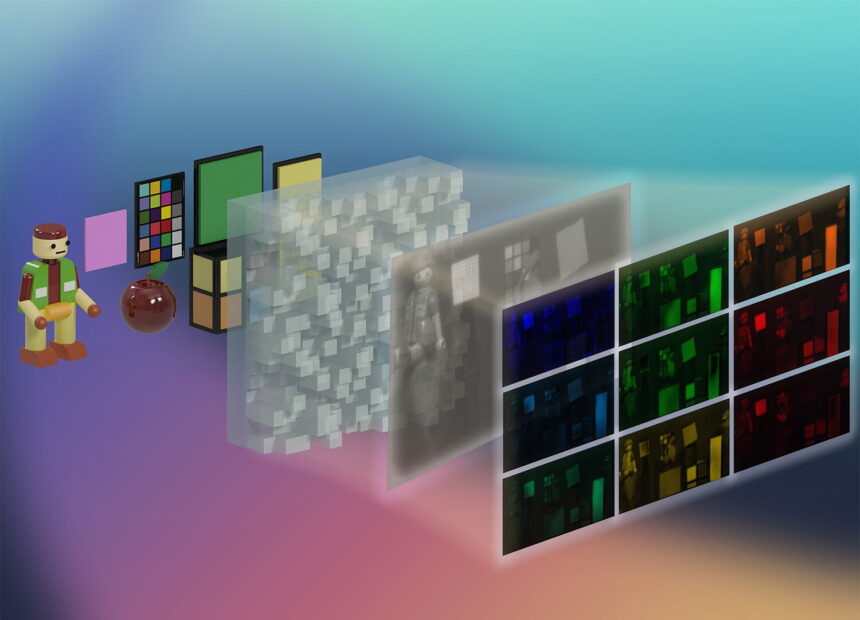
Now, researchers on the College of Utah’s John and Marcia Value School of Engineering have developed a brand new approach of taking a high-definition snapshot that encodes spectral knowledge into pictures, very similar to a conventional digital camera encodes colour. As an alternative of a filter that divides mild into three colour channels, their specialised filter divides it into 25. Every pixel shops compressed spectral info together with its spatial info, which pc algorithms can later reconstruct right into a “dice” of 25 separate pictures—every representing a definite slice of the seen spectrum.
This instantaneous encoding allows the researchers’ digital camera system—sufficiently small to suit right into a cellphone—to take high-definition video, and the compressed nature of the part pictures opens up new real-world purposes.
A research demonstrating the digital camera was led by Analysis Assistant Professor Apratim Majumder and Professor Rajesh Menon, each within the Division of Electrical & Laptop Engineering. The outcomes are reported within the journal Optica.
The digital camera’s design represents a leap ahead in how spectral knowledge might be captured.
“We introduce a compact digital camera that captures each colour and fantastic spectral particulars in a single snapshot, producing a ‘spectral fingerprint’ for each pixel,” Menon mentioned.
Hyperspectral cameras have lengthy been utilized in agriculture, astronomy and medication, the place delicate variations in colour could make a giant distinction. However these cameras have traditionally been cumbersome, costly and restricted to nonetheless pictures.
“After we began out on this analysis, our intention was to reveal a compact, quick, megapixel decision hyperspectral digital camera, in a position to document extremely compressed spatial-spectral info from scenes at video-rates, which didn’t exist,” Majumder mentioned.
The Utah staff’s breakthrough lies in the way it captures and processes the information. The important thing part is a diffractive aspect that’s positioned immediately over the digital camera’s sensor. It is the aspect’s repeating nanoscale patterns that diffract incoming mild and encodes each spatial and spectral info for every pixel on the sensor. By encoding the scene right into a single, compact two-dimensional picture moderately than a large three-dimensional knowledge dice, the digital camera makes hyperspectral imaging sooner and extra environment friendly.
“One of many major benefits of our digital camera is its means to seize the spatial-spectral info in a extremely compressed two-dimensional picture as a substitute of a three-dimensional knowledge dice and use subtle laptop algorithms to extract the total knowledge dice at a later level,” Majumder defined. “This enables for quick, extremely compressed knowledge seize.”
The streamlined method additionally cuts prices dramatically.
“Our digital camera prices many occasions much less, could be very compact and captures knowledge a lot sooner than most obtainable business hyperspectral cameras,” Majumder mentioned. “Now we have additionally proven the flexibility to post-process the information as per the necessity of the applying and implement totally different classifiers suited to totally different fields equivalent to agriculture, astronomy and bio-imaging.”
Information storage is one other benefit.
“Satellites would have hassle beaming down full picture cubes, however since we extract the cubes in post-processing, the unique recordsdata are a lot smaller,” Majumder added.
To reveal the digital camera’s capabilities, the researchers tried three real-world purposes: telling various kinds of tissue aside in a surgical scene; predicting the age of strawberries as they decayed over time; and mimicking a collection of spectral filters which can be utilized in astronomy.
The present prototype takes pictures at simply over one megapixel in measurement and might break them down into 25 separate wavelengths throughout the spectrum. However the staff is already engaged on enhancements.
“This work demonstrates a primary snapshot megapixel hyperspectral digital camera,” Majumder mentioned. “Subsequent, we’re creating a extra improved model of the digital camera that can enable us to seize pictures at a bigger picture measurement and elevated variety of wavelength channels, whereas additionally making the nano-structured diffractive aspect a lot less complicated in design.”
By making hyperspectral imaging cheaper, sooner, and extra compact, the U engineers have opened the door for applied sciences that might change the way in which we see the world and uncover particulars hidden throughout the spectrum.
Extra info:
Apratim Majumder et al, Excessive-definition (HD) snapshot diffractive computational spectral imaging and inferencing, Optica (2025). DOI: 10.1364/optica.559279
Quotation:
Compact digital camera makes use of 25 colour channels for high-speed, high-definition hyperspectral video (2025, September 25)
retrieved 25 September 2025
from https://techxplore.com/information/2025-09-compact-camera-channels-high-definition.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.