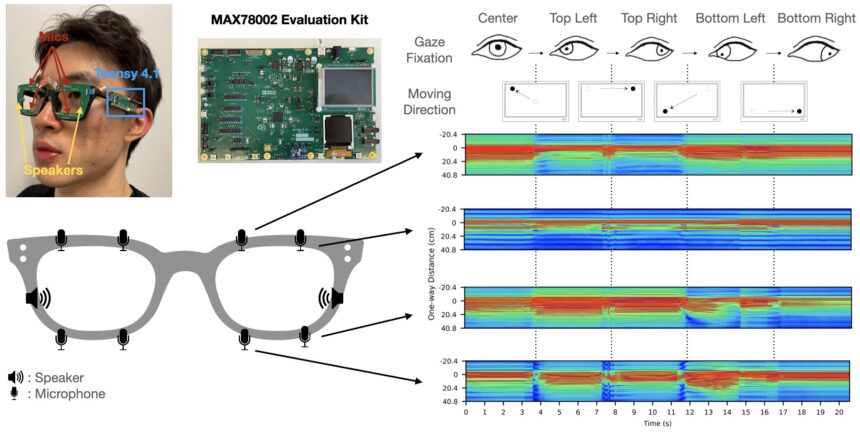
Cornell College researchers have developed two applied sciences that observe an individual’s gaze and facial expressions via sonar-like sensing. The know-how is sufficiently small to suit on business smartglasses or digital actuality or augmented actuality headsets but consumes considerably much less energy than related instruments utilizing cameras.
Each use audio system and microphones mounted on an eyeglass body to bounce inaudible soundwaves off the face and choose up mirrored indicators attributable to face and eye actions. One machine, GazeTrak, is the primary eye-tracking system that depends on acoustic indicators. The second, EyeEcho, is the primary eyeglass-based system to repeatedly and precisely detect facial expressions and recreate them via an avatar in real-time.
The units can final for a number of hours on a smartglasses battery and greater than a day on a VR headset.
“It is small, it is low cost and tremendous low-powered, so you’ll be able to put on it on smartglasses every single day—it will not kill your battery,” stated Cheng Zhang, assistant professor of data science. Zhang directs the Sensible Laptop Interfaces for Future Interactions (SciFi) Lab that created the brand new units.
“In a VR surroundings, you need to recreate detailed facial expressions and gaze actions so that you could have higher interactions with different customers,” stated Ke Li, a doctoral pupil who led the GazeTrak and EyeEcho improvement.
For GazeTrak, researchers positioned one speaker and 4 microphones across the inside of every eye body of a pair of glasses to bounce and choose up soundwaves from the eyeball and the realm across the eyes. The ensuing sound indicators are fed right into a personalized deep-learning pipeline that makes use of synthetic intelligence to deduce the route of the individual’s gaze repeatedly.
For EyeEcho, one speaker and one microphone are situated subsequent to the glasses’ hinges, pointing all the way down to catch pores and skin motion as facial expressions change. The mirrored indicators are additionally interpreted utilizing AI.
With this know-how, customers can have hands-free video calls via an avatar, even in a loud café or on the road. Whereas some smartglasses have the flexibility to acknowledge faces or distinguish between just a few particular expressions, presently, none observe expressions repeatedly like EyeEcho.
These two advances have functions past enhancing an individual’s VR expertise. GazeTrak may very well be used with display readers to learn out parts of textual content for folks with low imaginative and prescient as they peruse a web site.
GazeTrak and EyeEcho may additionally doubtlessly assist diagnose or monitor neurodegenerative ailments, like Alzheimer’s and Parkinsons. With these situations, sufferers typically have irregular eye actions and fewer expressive faces, and such a know-how may observe the development of the illness from the consolation of a affected person’s house.
Li will current GazeTrak on the Annual Worldwide Convention on Cell Computing and Networking within the fall and EyeEcho on the Affiliation of Computing Equipment CHI convention on Human Components in Computing Techniques in Could.
The findings are published on the arXiv preprint server.
Extra info:
Ke Li et al, GazeTrak: Exploring Acoustic-based Eye Monitoring on a Glass Body, arXiv (2024). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2402.14634
Quotation:
AI-powered ‘sonar’ on smartglasses tracks gaze, facial expressions (2024, April 10)
retrieved 13 April 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-04-ai-powered-sonar-smartglasses-tracks.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.