When two supplies come into contact, charged entities on their surfaces get a bit nudge. That is how rubbing a balloon on the pores and skin creates static electrical energy. Likewise, water flowing over some surfaces can acquire or lose cost.
Now, researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have harnessed the phenomenon to generate electrical energy from rain-like droplets transferring by way of a tube. They reveal a brand new type of stream that makes sufficient energy to gentle 12 LEDs.
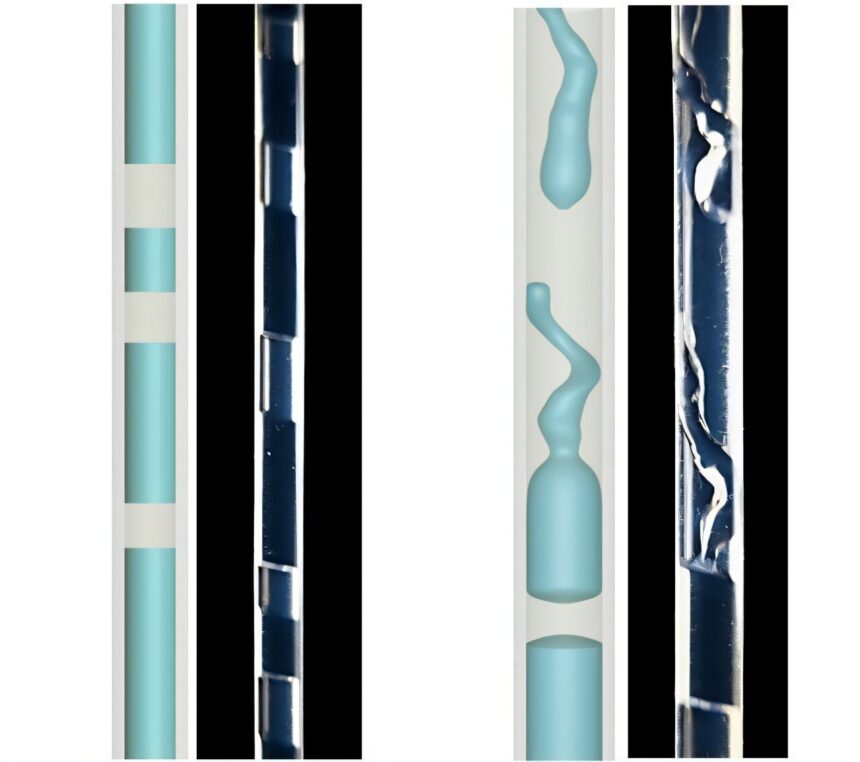
“Water that falls by way of a vertical tube generates a considerable quantity of electrical energy through the use of a particular sample of water stream: plug stream,” says Siowling Soh, the examine’s corresponding creator. “This plug stream sample may enable rain power to be harvested for producing clear and renewable electrical energy.”
When working water strikes a turbine, it generates electrical energy. Nevertheless, hydroelectricity is constrained to areas with giant volumes of water, like rivers. For smaller and slower volumes of water, an alternate is to harness cost separation, a phenomenon that produces electrical costs as water strikes by way of a channel with an electrically conductive internal floor. However cost separation is extraordinarily inefficient as a result of it’s restricted to the floor that the water strikes over.
Beforehand, scientists have tried to enhance its effectivity by making extra floor space out there by way of micro- or nanoscale channels for a steady stream of water. Nevertheless, water would not naturally go by way of such tiny channels, and if pumped, it requires extra power than will get generated. So, Soh, Chi Package Ao and colleagues wished to supply electrical energy utilizing bigger channels that rainwater may go by way of.
The staff designed a easy setup whereby water flowed out the underside of a tower by way of a metallic needle and spurted rain-sized droplets into the opening of a 12-inch-tall (32-centimeter-tall) and 2-millimeter-wide vertical polymer tube. The top-on collision of the droplets on the prime of the tube brought about a plug stream: quick columns of water interspersed with pockets of air.
As water flowed down the within of the tube, electrical costs separated. The water was then collected in a cup under the tube. Wires have been positioned on the prime of the tube and within the cup harvested the electrical energy.
The plug stream system transformed greater than 10% of the power of the water falling by way of the tubes into electrical energy. And in comparison with water flowing in a steady stream, plug stream produced 5 orders of magnitude extra electrical energy. As a result of the droplet speeds examined have been a lot slower than rain, the researchers counsel the system may very well be used to reap electrical energy from falling raindrops.
In one other experiment, the researchers noticed that transferring water by way of two tubes, both concurrently or sequentially, generated double the power. Utilizing this data, they channeled water by way of 4 tubes, and the setup powered 12 LEDs constantly for 20 seconds.
The researchers say that plug stream power may very well be less complicated to arrange and keep than hydroelectric energy vegetation, and it may very well be handy for city areas like rooftops.
Extra data:
Plug Move: Producing Renewable Electrical energy with Water from Nature by Breaking the Restrict of Debye Size, ACS Central Science (2025). DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.4c02110
Quotation:
A step towards harnessing clear power from falling rainwater (2025, April 16)
retrieved 18 April 2025
from https://techxplore.com/information/2025-04-harnessing-energy-falling-rainwater.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.