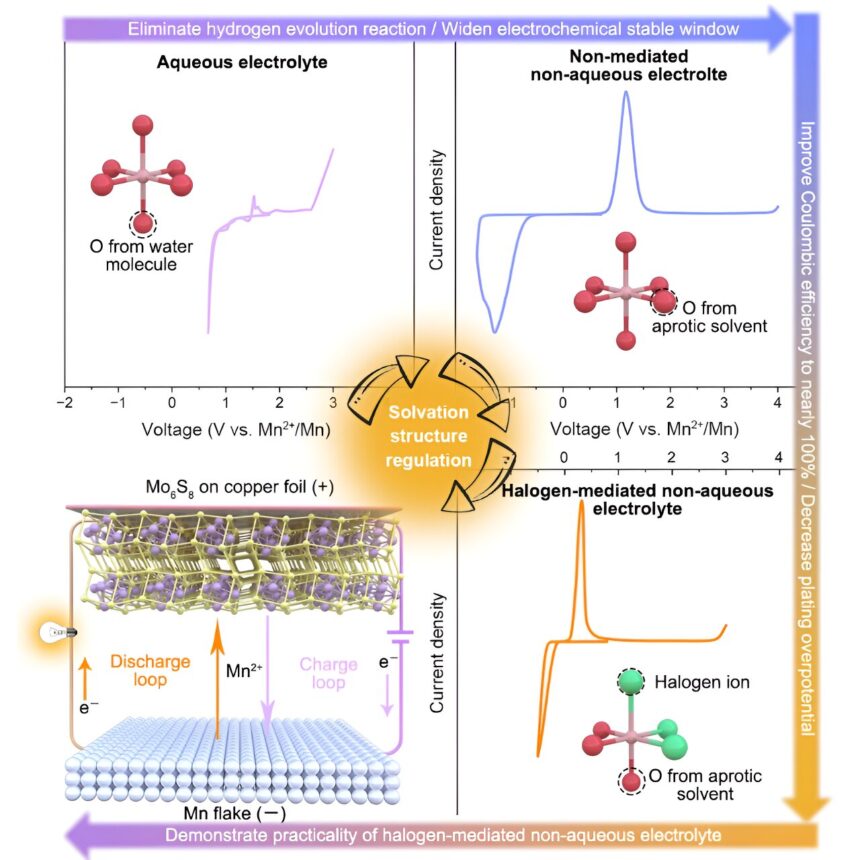
A analysis workforce led by Prof. Chen Wei from the College of Science and Expertise of China (USTC) of the Chinese language Academy of Science (CAS) revealed for the primary time the vital position of halogen-mediated solvation construction within the de-solvation technique of multivalent ions. The analysis consequence was published in Joule.
The workforce managed to make use of manganese steel batteries (MnMBs) because the analysis platform to totally reveal the vital position of halogen-mediated (with Cl as the principle analysis object) mechanism in decreasing the overpotential of the multivalent steel ions deposition and enhancing the Coulombic and the dissolution/deposition efficiencies.
With theoretical calculations and experiments, the researchers absolutely verified that Cl was absolutely concerned within the solvation of Mn2+ within the designed electrolyte, reworking [Mn(Osol)6]2+ solvated construction into [Mn(Osol)3Cl3]2+.
In contrast with different atoms, Cl atoms have a bigger radius and smaller cost density; thus, the solvated Mn-Cl bond is weaker than the Mn-O bond, vastly decreasing the de-solvation energies throughout deposition, decreasing the deposition overpotential of the manganese steel anode and considerably enhancing the Coulombic and Faraday efficiencies.
Researchers assembled symmetric and uneven cells to reveal the halogen-mediated electrolyte’s reliability. The experimental knowledge confirmed that the electrolyte can assist steady biking of symmetric cells for greater than 700 h at a present density of 0.1mA cm-2, which is much past the efficiency of the reported manganese-metal battery electrolytes.
The symmetric cells confirmed regular polarization values at completely different present densities, which absolutely demonstrated the wonderful multiplicity efficiency of the electrolyte. As well as, the electrolyte supplied a Coulombic effectivity near 100% and deposition/dissolution overpotentials of <200 mV even on completely different metallic or nonmetallic collectors.
An uneven cell assembled from this electrolyte will be stably cycled for greater than 1000h when making use of Ketjenblack (KB) as the present collector.
Remarkably, the manganese deposition/dissolution effectivity remained as excessive as 96.8%, even at a better floor capability (5 mAh cm-2).
To additional validate the worth of the designed halogen-mediated electrolyte, the researchers additionally developed a halogen-meditated non-aqueous manganese steel full cell. The cell was capable of cycle stably for almost 600 cycles within the designed halogen-mediated electrolyte and exhibited satisfying multiplicity efficiency and two well-defined plateaus.
The research presents a brand new path to develop rechargeable, non-aqueous MnMBs enabled by electrolyte engineering, which is anticipated to profit different multivalent steel batteries and electroplating industries.
Extra info:
Dongyang Shen et al, A chargeable, non-aqueous manganese steel battery enabled by electrolyte regulation, Joule (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.joule.2024.01.012
Offered by
College of Science and Expertise of China
Quotation:
A chargeable, non-aqueous manganese steel battery (2024, March 15)
retrieved 16 March 2024
from https://techxplore.com/information/2024-03-rechargeable-aqueous-manganese-metal-battery.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.